Abstract
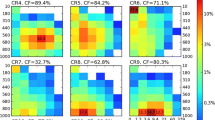
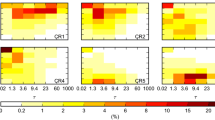
We take advantage of ISCCP simulator data available for many models that participated in CMIP5, in order to introduce a framework for comparing model cloud output with corresponding ISCCP observations based on the cloud regime (CR) concept. Simplified global CRs are employed derived from the co-variations of three variables, namely cloud optical thickness, cloud top pressure and cloud fraction (τ, p c , CF). Following evaluation criteria established in a companion paper of ours (Jin et al. 2016), we assess model cloud simulation performance based on how well the simplified CRs are simulated in terms of similarity of centroids, global values and map correlations of relative-frequency-of-occurrence, and long-term total cloud amounts. Mirroring prior results, modeled clouds tend to be too optically thick and not as extensive as in observations. CRs with high-altitude clouds from storm activity are not as well simulated here compared to the previous study, but other regimes containing near-overcast low clouds show improvement. Models that have performed well in the companion paper against CRs defined by joint τ–p c histograms distinguish themselves again here, but improvements for previously underperforming models are also seen. Averaging across models does not yield a drastically better picture, except for cloud geographical locations. Cloud evaluation with simplified regimes seems thus more forgiving than that using histogram-based CRs while still strict enough to reveal model weaknesses.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderberg MR (1973) Cluster analysis for applications. Elsevier, New York
Bodas-Salcedo A, Webb MJ, Bony S et al (2011) COSP: satellite simulation software for model assessment. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 92:1023–1043. doi:10.1175/2011BAMS2856.1
Bony S, Webb M, Bretherton CS et al (2011) CFMIP: towards a better evaluation and understanding of clouds and cloud feedbacks in CMIP5 models. CLIVAR Exch 56(16):20–24
Chen T, Rossow WB, Zhang Y (2000) radiative effects of cloud-type variations. J Clim 13:264–286. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<0264:REOCTV>2.0.CO;2
Dolinar EK, Dong X, Xi B et al (2015) Evaluation of CMIP5 simulated clouds and TOA radiation budgets using NASA satellite observations. Clim Dyn 44:2229–2247. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2158-9
Garay MJ, de Szoeke SP, Moroney CM (2008) Comparison of marine stratocumulus cloud top heights in the southeastern Pacific retrieved from satellites with coincident ship-based observations. J Geophys Res 113:D18204. doi:10.1029/2008JD009975
Gordon ND, Norris JR, Weaver CP, Klein SA (2005) Cluster analysis of cloud regimes and characteristic dynamics of midlatitude synoptic systems in observations and a model. J Geophys Res 110:D15S17. doi:10.1029/2004JD005027
Jin D, Oreopoulos L, Lee D (2016) Regime-based evaluation of cloudiness in CMIP5 models. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-016-3064-0
Kay JE, Hillman BR, Klein SA et al (2012) Exposing global cloud biases in the community atmosphere model (CAM) using satellite observations and their corresponding instrument simulators. J Clim 25:5190–5207. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00469.1
Klein SA, Jakob C (1999) Validation and sensitivities of frontal clouds simulated by the ECMWF nodel. Mon Weather Rev 127:2514–2531. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1999)127<2514:VASOFC>2.0.CO;2
Klein SA, Zhang Y, Zelinka MD et al (2013) Are climate model simulations of clouds improving? An evaluation using the ISCCP simulator. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:1329–1342. doi:10.1002/jgrd.50141
Luo S, Sun Z, Zheng X et al (2015) Evaluation of ACCESS model cloud properties over the Southern Ocean area using multiple-satellite products. Q J R Meteorol Soc. doi:10.1002/qj.2641
MacQueen J (1967) Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability. Oakland, CA, USA, pp 281–297
Nam C, Bony S, Dufresne J-L, Chepfer H (2012) The “too few, too bright” tropical low-cloud problem in CMIP5 models. Geophys Res Lett 39:L21801. doi:10.1029/2012GL053421
Pincus R, Batstone CP, Hofmann RJP et al (2008) Evaluating the present-day simulation of clouds, precipitation, and radiation in climate models. J Geophys Res 113:D14209. doi:10.1029/2007JD009334
Pincus R, Platnick S, Ackerman SA et al (2012) Reconciling simulated and observed views of clouds: MODIS, ISCCP, and the limits of instrument simulators. J Clim 25:4699–4720. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00267.1
Rossow WB, Schiffer RA (1991) ISCCP cloud data products. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 72:2–20. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1991)072<0002:ICDP>2.0.CO;2
Rossow WB, Schiffer RA (1999) Advances in understanding clouds from ISCCP. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 80:2261–2287. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1999)080<2261:AIUCFI>2.0.CO;2
Rossow WB, Tselioudis G, Polak A, Jakob C (2005) Tropical climate described as a distribution of weather states indicated by distinct mesoscale cloud property mixtures. Geophys Res Lett 32:L21812. doi:10.1029/2005GL024584
Taylor KE, Stouffer RJ, Meehl GA (2012) An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 93:485–498. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1
Tselioudis G, Rossow W, Zhang Y, Konsta D (2013) Global weather states and their properties from passive and active satellite cloud retrievals. J Clim 26:7734–7746. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00024.1
Tsushima Y, Ringer MA, Webb MJ, Williams KD (2013) Quantitative evaluation of the seasonal variations in climate model cloud regimes. Clim Dyn 41:2679–2696. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1609-4
Webb M, Senior C, Bony S, Morcrette J-J (2001) Combining ERBE and ISCCP data to assess clouds in the Hadley Centre, ECMWF and LMD atmospheric climate models. Clim Dyn 17:905–922
Williams KD, Tselioudis G (2007) GCM intercomparison of global cloud regimes: present-day evaluation and climate change response. Clim Dyn 29:231–250. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0232-2
Williams KD, Webb MJ (2009) A quantitative performance assessment of cloud regimes in climate models. Clim Dyn 33:141–157. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0443-1
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the World Climate Research Programme’s Working Group on Coupled Modeling, which is responsible for CMIP, and we thank the climate modeling groups (listed in Table 1 of this paper) for producing and making available their model output. For CMIP, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison provides coordinating support and led development of software infrastructure in partnership with the Global Organization for Earth System Science Portals. Lastly, funding by NASA’s Modeling Analysis and Prediction (MAP) program is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, D., Oreopoulos, L. & Lee, D. Simplified ISCCP cloud regimes for evaluating cloudiness in CMIP5 models. Clim Dyn 48, 113–130 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3107-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3107-6