Abstract
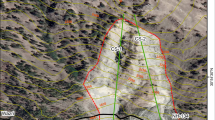
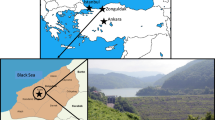
Fault movement in dam foundations is an earthquake hazard feature that may lead to severe structural distortions. Such movements may manifest as rock failures, crushing and displacements of rock masses. Faults with surface breaking and potential block movements are also of considerable interest in the issue of dam safety. The Upper Gotvand Dam is the highest rock fill dam in Iran which was constructed over the Karun River in the Khuzestan Province, southwest Iran. Its location in the Zagros active belt, the most active seismotectonic zone of the country, makes it prone to abutment instability and potential seepage through the foundation and abutments. The dam foundation is on the sandstones of the Agha-Jari Formation while the abutments are composed of rock mass of the Bakhtyari Formation. The right abutment of the dam is highly fractured and displaced due to action of the Pir-Ahmad active fault.. Geotechnical sections along the dam axis and across the right abutment indicate four strike faults near the right bank as well as sharp changes in the dip of bedding along the dam axis. The Agha-Jari layers are tightly folded beneath the dam axis with a 30° inter-limb angle forming a chevron fold. The geomechanical classification of the outcropped rocks is in the range of weak to very weak. The whole region is affected by an N-S basement tectonic lineament introduced in this research as the Lali-Ahvaz trend. Variations in the geotechnical properties of the dam site are mostly due to the movement of the Pir-Ahmad Fault. The activity of the fault should be re-assessed for future operations and producing dam maintenance plans as fault activity could diminish future dam safety.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi, M., Rostami, M. and Mahmoodi Dovom Niasar, H. (2008) Time dependent behavior of the Upper Gotvand dam foundation (in Persian). Proc. 2nd National. Conf. on Dam and Hydropower Plants, IWPCO, Tehran, Iran, 8p
Ahmadi, T., Rahimi-Chakdel, A and Barjasteh, A. (2012) Investigation of the active tectonics of Lali-Gotvand region using channel length, and drainage basin asymmetry indices (in Persian). Proc. 16th Symp. Geol .Soc. Iran, 4–6 Sept. Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran, 8p
Ajalloeian R, Fatehi L, Ganjalipour K (2011) Evaluation of hydrojacking and hydrofracturing behavior in Aghajari formation (Gotvand dam site foundation), Iran. J Geol Mining Res 3(3):46–53
Aminpour, M., Noorzad, A., and Mahboobi Ardekani, A.R, (2008) Investigation and comparison of common and developed numerical techniques in analysis of rock slope stability, case study of the Gotvand dam northern abutment (in Persian). Proc. 2nd National. Conf. on Dam and Hydropower Plants, IWPCO, Tehran, Iran, 9p
Barjasteh, A, (1994) Morphotectonics and its role on Karun River evolution (in Persian). Abstracts. 3rd Seminar on River Engineering, Ahvaz University, Ahvaz, Iran, p 122
Barjasteh, A., (2009) Geotechnical constraints for Dez Dam development project in southwest of Iran. 23rd ICOLD Congress, 23–30 May, Brazil, 12 pp
Barjasteh, A. (2012) Salt Tectonics Impact on Dam Construction in Khuzestan Province of Iran. Proc. 24th ICOLD congress. Kyoto, Japan, 6p
Barjasteh, A. (2013) Geologic structure control on seepage potential of the Upper Gotvand Dam, Iran. 81st ICOLD annual meeting. Seattle, USA, p 9
Berberian, M. (1995) Master "blind" thrust faults hidden under the Zagros folds: active basement tectonics and surface morphotectonics. Tectonophysics, 241. pp. 193-224.
Edgell HS (1996) Salt tectonism in the Persian Gulf Basin. Geol Soc Lond, Spec Publ 100:129–151
Falcon, N.I. (1974) Southern Iran, Zagros Mountains, In : Spencer, AM (ed), Mesozoic – Cenozoic Orogenic Belts, Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. No. 4, p 199–211
Gutiérrez, F., and Lizaga, I, (2016) Sinkholes, collapse structures and large landslides in an active salt dome submerged by a reservoir: The unique case of the Ambal ridge in the Karun River, Zagros Mountains, Iran. Geomorphology, Volume 254, p. 88-103.
Haji Poor, Y., Barjasteh, A., Yazdjerdi, K., Daneshian, H. (2010) Analysis of Fracture System in Gachsaran Formation in Lali-Gotvand Region (north of Dezful Embayment). (In Persian) 28th Symposium on Geosciences of GSI and 14th Symp. Geol .Soc. Iran, 20–22 Feb. Uromieh University, Uromieh, Iran. 6p
Huber, H. 1977. Explanatory notes to geological map of Iran. National Iranian Oil Company, Exploration and Production Group, GR 340, 1-170, (unpublished)
Jamison JW (1987) Geometric analysis fold development in overthrust tranes. J Struct Geol 9:207–219
Keller EA, Pinter N (1996) Active tectonics: earthquakes, uplift and landforms. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Khosravi, F. (2000) Dam site selection on problematic foundation with slickensides (in Persian). Proc. 4th NIRCOLD Conf. On Dam Construction, Ministry of Energy, Tehran, pp.636–644
Maggi A, Priestly K, Jackson J (2003) Focal depths of moderate and large site earthquakes in Iran. J Seismol Earthquake Eng 4:1–10
Mahboubi, A., Aminpour, M., and Noorzad, A. (2008) Conventional and advanced numerical methods of rock slope stability analysis, A comparison study, Gotvand Dam right abutment (Iran) Case Study. Proc. 12th International Conference of International Association for Computer Methods and Advances in Geomechanics (IACMAG), 1–6 October, 2008. Goa, India. 9
Mahinroosta R, Alizadeh A, Gatmiri B (2015) Simulation of collapse settlement of first filling in a high rockfill dam. J Eng Geol 187:33–42
Mahmoodi Dovom Niasar H, Farough Hossieini M, Ahmadi M, Jalali ME (2010) Investigation of the role of dam weight on time dependent behavior of the upper Gotvand dam foundation (in Persian). Omran Modarres Sci Res J 2:13
Maleki, E., and Behnam, M, (2005) Seismic Aspects of Cascading Dams Constructed on Karun River. 73rd ICOLD annual meeting. Tehran, Iran, 10
Mehryar, M.A., and Taghvaeian, A. (2014) Rock piezometer installation in the Artesian boreholes of the Upper Gotvand dam), (in Persian). Proc. 1st National. Conf. on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Shahid Rajaee Teacher Training University, Tehran, Iran, 9
Mohammad, S., Rohani, S.Y., Ganjian, N., and Rahimi-Dizadji, M. (2014) Multiple Water-Tightening Systems in the Foundation of Upper Gotvand Dam, Southern Iran. Proc. 24th ICOLD Int. Symp. On Dams in a Global Environmental Challenges. Bali, Indonesia, p 14
Mottaghi F, Yassaghi A (2012) Investigation of the effect of Gachsaran formation on fold style of the overlying rock units in Lali, Papileh and Zilaie oilfields, Zagros fold-Thrust Belt (in Persian). Adv Appl Geol J Chamran University of Ahvaz 1(4):71–81
Nateghi, R., and Kiyani, M. (2008) Application of DEM technique in estimation of seepage and water tightening limit in dam sites (case study of the Upper Gotvand dam), (in Persian). Proc. 2nd National. Conf. on Dam and Hydropower Plants, IWPCO, Tehran, Iran, 8p
N.I.O.C, (1967) Geological map of Shushtar, 1: 100000
Pattinson, R., and Jazayeri, B. (1972) Structural Analysis of Zagros Anticlines. I.O.O.C., Internal Report No. 1188, p 78
Shahrokhi, Z. (2000) Application of rock mass classification in determination of geotechnical parameters of the Upper Gotvand Dam (in Persian). Proc. 4th NICOLD Conf. On Dam Construction, Ministry of Energy, Tehran, pp.840–861
Sharifi Boroujerdi, M., Salehi, D., Hazrati, M., Mahjoub, D. (2012) Dynamic stability analysis of the Upper Gotvand dam right abutment against earthquake (in Persian). Proc. 1st Int. and 3rd National. Conf. on Dam and Hydropower Plants, IWPCO, Tehran, Iran, 9p
Sharifzadeh M, Nateghi R, Kiyani M (2008) Hydro-mechanical modeling of seepage in Gotvand dam foundation. In: Shao J-F, Burlion N (eds) Thermo-Hydromechanical and chemical coupling in Geomaterials and applications: proceedings of the 3rd international symposium GeoProc'2008. Wiley, Hoboken
Tatar, M. (2012) Seismicity and seismotectonics in the Upper Gotvand dam region, (in Persian). Proc. 1st Int. and 3rd National. Conf. on Dam and Hydropower Plants, IWPCO, Tehran, Iran, 10p
Twiss RJ, Moores EM (1992) Structural Geology. W. H. Freeman & Co., San Francisco, p 532
Van der Pluijm, B.A., and Marshak, S. (2004) Earth Structure (2nd edition); An introduction to structural geology and tectonics. W. W. Norton & Company. 673p
Van Os, B., Rouaix, S.J., Hulstrand, R.F., Ghashghai, M. and Movsessian, A.I. (1965) Dezful Embayment Geological Survey 1961–1963. I.O.O.C., Internal Report No. 1044, 84p
Yaghoobi Rafi, J. (2010) Applying “Real Time Grouting Control Method” in Sedimentary Rock with Gotvand Dam unpublished M.Sc. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). 107p
Yaghoobi Rafi, J. (2013) Design approach for grouting of rock fractures; theory and practice. BeFo Report 124. Rock Engineering Research Foundation. 58p
Yazdinejad, H.R., Hashemi, S., and Moradi, M. (2007) Evaluation of groutability and permeability relationship in Gotvand Dam. Proc. 3rd Iranian Rock Mechanics Conference (in Persian). Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, October 3–5, 2005, Iran, 6p
Zafarani, H., Noorzad, A., Soleymani, S., and Ansari, A. (2005) Generation of near-fault response spectrum of Gotvand Dam by considering uncertainty in mathematical framework. Proc. 73rd ICOLD annual meeting. Tehran, May 1–6, 2005, Iran, 10p
Ziaie Moayed R, Izadi E, Fazlavi M (2012) In-situ stress measurements by hydraulic fracturing method at Gotvand dam site. Iran Turkish J Eng Env Sci 36(2012):179–194
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Dr. Gh. A. Kazemi of Shahrood University of Technology for valuable comments on the original manuscript. He also appreciates two unknown reviewers for their comprehensive comments and corrections that improved the original manuscript. The author also thanks Mrs. Roya Ghilav of the Technical Office, Khuzestan Water & Power Authority (KWPA) for helping in the review and correcting the English version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barjasteh, A. The impact of active faulting on the geotechnical properties of the Upper Gotvand Dam, southwest Iran. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78, 709–722 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1163-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1163-8