Abstract
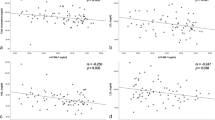
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory and systemic disease characterized by endothelial activation. The main objective of this study was to verify the profile of cell adhesion molecules (CAM) in RA patients, and the influence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and drugs used in the treatment of RA in this profile. A second objective was to propose models of prediction of activity in RA using these biomarkers. A total of 115 healthy individuals and 144 RA patients were enrolled. Disease activity was determined by DAS28 (disease activity score 28) based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) or C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP). Serum CAM and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1), anthropometric and immunological parameters were measured. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) was significantly decreased, and PAI-1 was significantly higher in RA patients as compared to controls. Binary logistic regression analysis showed that VCAM-1, CRP, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) predicted RA with a sensitivity of 95.9% and a specificity of 89.5%. 42.9% of the variance in DAS28-ESR and 49.2% of the variance in DAS28-CRP are explained by increased PAI-1, TNF-α, body mass index (BMI) and decreased platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM-1). Our data show that lower levels of VCAM-1 are associated with RA independently of MetS, while increased PAI-1 levels were associated with both RA and MetS and increased selectins (E-selectin and P-selectin) were exclusively associated with MetS and not with RA. A model to predict disease activity based on PECAM-1, PAI-1, TNF-α, age and BMI is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chimenti MS, Triggianese P, Conigliaro P, Candi E, Melino G, Perricone R. The interplay between inflammation and metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6(9):e1887.
McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205–19.
Angelotti F, Parma A, Cafaro G, Capecchi R, Alunno A, Puxeddu I. One year in review 2017: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35:368–78.
Ursini F, Leporini C, Bene F, D’Angelo S, Mauro D, Russo E, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha agents and endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5346.
Mojcik CF, Shevach EM. Adhesion molecules. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40(6):991–1004.
Yang X, Chang Y, Wei W. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation: immunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:1–9.
Springer TA. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990;346:425–34.
Wai Wong C, Dye DE, Coombe DR. The role of immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules in cancer metastasis. Int J Cell Biol. 2012;2012:340296.
Prasad M, Hermann J, Gabriel SE, Weyand CM, Mulvagh S, Mankad R, et al. Cardiorheumatology: cardiac involvement in systemic rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015;12(3):168–76.
Bartoloni E, Shoenfeld Y, Gerli R. Inflammatory and autoimmune mechanisms in the induction of atherosclerotic damage in systemic rheumatic diseases: two faces of the same coin. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63(2):178–83.
Blann AD, Herrick A, Jayson MI. Altered levels of soluble adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis and systemic sclerosis. Br J Rheumatol. 1995;34(9):814–9.
Veale DJ, Maple C, Kirk G, McLaren M, Belch JJ. Soluble cell adhesion molecules-P-selectin and ICAM-1, and disease activity in patients receiving sulphasalazine for active rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27(0300–9742 (Print)):296–9.
Ateş A, Kinikli G, Turgay M, Duman M. Serum-soluble selectin levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2004;23(5):421–5.
Wang L, Ding Y, Guo X, Zhao Q. Role and mechanism of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10:1229–33.
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet. 2005;365(9468):1415–28.
Zambon A, Pauletto P, Crepaldi G. Review article: the metabolic syndrome–a chronic cardiovascular inflammatory condition. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22(Suppl 2):20–3.
Schram MT, Stehouwer CD. Endothelial dysfunction, cellular adhesion molecules and the metabolic syndrome. Horm Metab Res. 2005;37(1):49–55.
Kamper EF, Kopeikina LT, Trontzas F, Potamianou A, Tsakiroglou E, Stavridis JC. The effect of disease activity related cytokines on the fibrinolytic potential and cICAM-1 expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(11):2545–50.
Medcalf RL. Fibrinolysis, inflammation, and regulation of the plasminogen activating system. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(SUPPL. 1):132–42.
Gonzales-Gay MA, Garcia-Unzueta MT, De Matias JM, Gonzales-Juanatey C, Garcia-Porrua C, Sanchez-Andrade A, et al. Influence of anti-TNF-α infliximab therapy on adhesion molecules associated with atherogenesis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006;24(4):373–9.
Södergren A, Karp K, Boman K, Eriksson C, Lundström E, Smedby T, et al. Atherosclerosis in early rheumatoid arthritis: very early endothelial activation and rapid progression of intima media thickness. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):R158.
Da Cunha V, Brenol C, Brenol J, Fuchs S, Arlindo E, Melo I, et al. Metabolic syndrome prevalence is increased in rheumatoid arthritis patients and is associated with disease activity. Scand J Rheumatol. 2012;41(3):186–91.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1580–8.
Prevoo MLL, MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LBA, van Riel PLCM. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Arthritis Rheum. 1995,38(1):44-48.
Prevoo MLL, van´t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LBA, van Riel PLCM, Prevoo MLL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38(1):44–8.
Fransen J, Welsing P, Keijzer RD, Riel PV. Disease activity scores using C-reactive protein: CRP may replace ESR in the assessment of RA disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;62:151.
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute scientific statement. Circulation. 2005;112(17):2735–52.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y, Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B. 1995;57(1):289–300.
Volin MV. Soluble adhesion molecules in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:633–53.
Gómez Rosso L, Benítez MB, Fornari MC, Berardi V, Lynch S, Schreier L, et al. Alterations in cell adhesion molecules and other biomarkers of cardiovascular disease in patients with metabolic syndrome. Atherosclerosis. 2008;199(2):415–23.
Kolopp-Sarda MN, Guillemin F, Chary-Valckenaere I, Béné MC, Pourel J, Faure GC. Longitudinal study of rheumatoid arthritis patients discloses sustained elevated serum levels of soluble CD106 (V-CAM). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001;19(2):165–70.
Littler AJ, Buckley CD, Wordworth P, Collins I, Martinson J, Simmons DL. A distinct profile of six soluble adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, ICAM-3, VCAM-1, E-selectin, L-selectin and P-selectin) in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1997;36(2):164–9.
Machold KP, Kiener HP, Graninger W, Graninger WB. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993;68(1):74–8.
Kopeikina LT, Kamper EF, Koutsoukos V, Bassiacos Y, Stavridis I. Imbalance of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) and its specific inhibitor (PAI-1) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis associated with disease activity. Clin Rheumatol. 1997;16(3):254–60.
Wallberg-Jonsson S, Cvetkovic JT, Sundqvist KG, Lefvert K, Rantapää-Dahlqvist SJ. Activation of the immune system and inflammatory activity in relation to markers of atherothrombotic disease and atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2002;29(5):875–82.
Mertens I, Verrijken A, Michiels JJ, Van der Planken M, Ruige JB, Van Gaal LF. Among inflammation and coagulation markers, PAI-1 is a true component of the metabolic syndrome. Int J Obes. 2006;30(8):1308–14.
Chou YY, Sheu WHH, Tang YJ, Chen YM, Liao SC, Chuang YW, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) is a valuable biomarker for predicting the metabolic syndrome (MS) in institutionalized elderly residents in Taiwan. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2009;49(SUPPL.2):S41–5.
Coffey CS, Asselbergs FW, Hebert PR, Hillege HL, Li Q, Moore JH, et al. The association of the metabolic syndrome with PAI-1 and t-PA Levels. Cardiol Res Pract. 2011;2011:1–8.
Bilgili S, Celebiler AC, Dogan A, Karaca B. Inverse relationship between adiponectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in metabolic syndrome patients. Endocr Regul. 2008;42:63–8.
Ahirwar AK, Jain A, Singh A, Goswami B, Bhatnagar MK, Bhatacharjee J. The study of markers of endothelial dysfunction in metabolic syndrome. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2015;24(3):131–6.
Srikanthan K, Feyh A, Visweshwar H, Shapiro JI, Sodhi K. Systematic review of metabolic syndrome biomarkers: a panel for early detection, management, and risk stratification in the West Virginian population. Int J Med Sci. 2016;13(1):25–38.
Alessi MC, Juhan-Vague I. PAI-1 and the metabolic syndrome links, causes, and consequences. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2200–7.
Costa NT, Iriyoda TMV, Kallaur AP, Delongui F, Alfieri DF, Lozovoy MAB, et al. Influence of insulin resistance and TNF-α on the inflammatory process, oxidative stress, and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016(Das 28):1–9.
Cook-Mills JM, Marchese ME, Abdala-Valencia H. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and signaling during disease: regulation by reactive oxygen species and antioxidants. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(6):1607–38.
Chiu JJ, Lee PL, Chen CN, Lee CI, Chang SF, Chen LJ, et al. Shear stress increases ICAM-1 and decreases VCAM-1 and E-selectin expressions induced by tumor necrosis factor-α in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(1):73–9.
Ugur M, Yildirim K, Kiziltunc A, Erdal A, Karatay S, Senel K. Correlation between soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 level and extracellular superoxide dismutase activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a possible association with disease activity. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33(4):239–43.
Klimiuk PA, Sierakowski S, Latosiewicz R, Cylwik JP, Cylwik B, Skowronski J, et al. Soluble adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in patients with distinct variants of rheumatoid synovitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61(9):804–9.
Klimek E, Skalska A, Kwaśny-Krochin B, Surdacki A, Sulicka J, Korkosz M, et al. Differential associations of inflammatory and endothelial biomarkers with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis of short duration. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014.
Kaur J. A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract. 2014;2014:943162.
Han TS, Lean ME. A clinical perspective of obesity, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis. 2016;5:204800401663337.
Scavuzzi BM, Simão ANC, Iryioda TMV, et al. Increased lipid and protein oxidation and lowered antioxidant defenses in systemic lupus erythematosus are associated with severity of illness, autoimmunity, increased adhesion molecules and Th1 and Th17 immune shift. Immunol Res. 2018;66(1):158–71.
Peduzzi P, Concato J, Kemper E, Holford TR, Feinstein AR. A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996;49(12):1373–9.
Vittinghoff E, McCulloch CE. Relaxing the rule of ten events per variable in logistic and Cox regression. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;165(6):710–8.
van Smeden M, de Groot JHA, Moons KGM, Collins GS, Altman DG, Eijkemans MJC, et al. No rationale for 1 variable per 10 events criterion for binary logistic regression analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16:163.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Council of Brazilian Research-CNPq and by Araucária Foundation from the state of Paraná. We thank the University Hospital of State University of Londrina and HUTec Foundation for technical and administrative supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All the participants included in this study provided written informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Sá, M.C., Simão, A.N.C., de Medeiros, F.A. et al. Cell adhesion molecules and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: influence of metabolic syndrome. Clin Exp Med 18, 495–504 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-018-0516-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-018-0516-3