Abstract
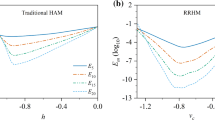
We have deduced an iteration scheme in the incremental harmonic balance (IHB) method using the harmonic balance plus the Newton-Raphson method. Since the convergence of the iteration is dependent upon the initial values in the iteration, the convergent region is greatly restricted for some cases. In this contribution, in order to enlarge the convergent region of the IHB method, we constructed the zeroth-order deformation equation using the homotopy analysis method, in which the IHB method is employed to solve the deformation equation with an embedding parameter as the active increment. Taking the Duffing and the van der Pol equations as examples, we obtained the highly accurate solutions. Importantly, the presented approach renders a convenient way to control and adjust the convergence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lau S.L., Cheung Y.K.: Amplitude incremental variational principle for nonlinear vibration of elastic systems. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 48, 959–964 (1981)
Ferri A.A.: On the equivalence of the incremental harmonic balance method and the harmonic balance-Newton Raphson method. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 53, 455–457 (1986)
Lau S.L., Cheung Y.K., Wu S.Y.: Incremental harmonic balance method with multiple time scales for aperiodic vibration of nonlinear system. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 50, 871–876 (1983)
Lau S.L., Cheung Y.K., Wu S.Y.: Nonlinear vibration of thin elastic plates, part 1: Generalized incremental Hamilton’s principle and element formulation; part 2: Internal resonance by amplitude-incremental finite element. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 51, 837–851 (1984)
Cheung Y.K., Chen S.H., Lau S.L.: Application of the incremental harmonic balance method to cubic non-linearity systems. J. Sound Vib. 140, 273–286 (1990)
Lau S.L., Yuen S.W.: The Hopf bifurcation and limit cycle by the incremental harmonic balance method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 91, 1109–1121 (1991)
Lau S.L., Yuen S.W.: Solution diagram of nonlinear dynamic-systems by IHB method. J. Sound Vib. 167, 303–316 (1993)
Raghothama A., Narayanan S.: Non-linear dynamics of a two-dimensional airfoil by incremental harmonic balance method. J. Sound Vib. 226, 493–517 (1999)
Xu L., Lu M.W., Cao Q.: Bifurcation and chaos of a harmonically excited oscillator with both stiffness and viscous damping piecewise linearities by incremental harmonic balance method. J. Sound Vib. 264, 873–882 (2003)
Sarkar S., Venkatraman K.: A numerical technique to predict periodic and quasi-periodic response of nonlinear dynamic systems. Comput. Struct. 81, 1383–1393 (2003)
Liao S.J.: A second-order approximate analytical solution of a simple pendulum by the process analysis method. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 59, 970–975 (1992)
Liao S.J.: An approximate solution technique not depending on small parameters: A special example. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 30, 371–380 (1995)
Liao S.J.: A kind of approximate solution technique which does not depend upon small parameters—II: an application in fluid mechanics. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 32(5), 815–822 (1997)
Liao S.J., Chwang A.T.: Application of homotopy analysis method in nonlinear oscillations. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 65(4), 914–922 (1998)
Liao S.J.: An explicit, totally analytic approximate solution for Blasius’ viscous flow problems. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 34, 759–778 (1999)
Liao S.J.: An analytic approximate approach for free oscillations of self-excited system. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 39, 271–280 (2003)
Liao S.J.: On the homotopy analysis method for nonlinear problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 147, 499–513 (2004)
Mehmood A., Ali A.: Analytic homotopy solution of generalized three-dimensional channel flow due to uniform stretching of the plate. Acta Mech. Sin. 23, 503–510 (2007)
Asghar S., Mudassar Gulzar M., Ayub M.: Effects of partial slip on flow of a third grade fluid. Acta Mech. Sin. 22, 393–396 (2006)
Abbasbandy S.: The application of homotopy analysis method to solve a generalized Hirota-Satsuma coupled KdV equation. Phys. Lett. A 361, 478–483 (2007)
Liao S.J., Tan Y.: A general approach to obtain series solutions of nonlinear differential equations. Stud. Appl. Math. 119, 297–354 (2007)
Hayat T., Sajid M.: On analytic solution for thin film flow of a forth grade fluid down a vertical cylinder. Phys. Lett. A 361, 316–322 (2007)
Sajid M., Hayat T., Asghar S.: Comparison between the HAM and HPM solutions of tin film flows of non-Newtonian fluids on a moving belt. Nonlinear Dyn. 50(1–2), 27–35 (2007)
Chen Y.M., Liu J.K.: Homotopy analysis method for limit cycle flutter of airfoils. Appl. Math. Comput. 203(2), 854–863 (2008)
Wen J.M., Cao Z.C.: Nonlinear oscillations with parametric excitation solved by homotopy analysis method. Acta Mech. Sin. 24, 325–329 (2008)
Chen Y.M, Liu J.K.: A study of homotopy analysis method for limit cycle of van der Pol equation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14, 1416–1421 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10772202), Doctoral Program Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20050558032), and Guangdong Province Natural Science Foundation (07003680, 05003295).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Liu, J. Improving convergence of incremental harmonic balance method using homotopy analysis method. Acta Mech Sin 25, 707–712 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0256-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0256-4