Abstract
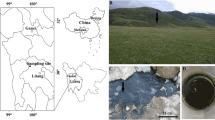
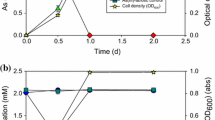
Biological arsenic oxidation has been suggested as a key biogeochemical process that controls the mobilization and fate of this metalloid in aqueous environments. To the best of our knowledge, only four aerobic chemolithoautotrophic arsenite-oxidizing (CAO) bacteria have been shown to grow via direct arsenic oxidation and to have the essential genes for chemolithoautotrophic arsenite oxidation. In this study, a new CAO bacterium was isolated from a high Andean watershed evidencing natural dissolved arsenic attenuation. The bacterial isolate, designated TS-1, is closely related to the Ancylobacter genus, in the Alphaproteobacteria class. Results showed that TS-1 has genes for arsenite oxidation and carbon fixation. The dependence of bacterial growth from arsenite oxidation was demonstrated. In addition, a mathematical model was suggested and the kinetic parameters were obtained by simultaneously fitting the biomass growth, arsenite depletion curves, and arsenate production. This research increases the knowledge of chemolithoautotrophic arsenic oxidizing microorganisms and its potential role as a driver for natural arsenic attenuation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achour AR, Bauda P, Billard P (2007) Diversity of arsenite transporter genes from arsenic-resistant soil bacteria. Res Microbiol 158(2):128–137
Alfreider A, Vogt C, Hoffmann D, Babel W (2003) Diversity of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large-subunit genes from groundwater and aquifer microorganisms. Microb Ecol 45(4):317–328
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Andreoni V, Zanchi R, Cavalca L, Corsini A, Romagnoli C, Canzi E (2012) Arsenite oxidation in Ancylobacter dichloromethanicus As3-1b strain: detection of genes involved in arsenite oxidation and CO2 fixation. Curr Microbiol 65(2):212–218
Andres J, Bertin PN (2016) The microbial genomics of arsenic. Fems Microbiol Rev 40(2):299–322
Battaglia-Brunet F, Joulian C, Garrido F, Dictor M-C, Morin D, Coupland K, Johnson DB, Hallberg KB, Baranger P (2006) Oxidation of arsenite by Thiomonas strains and characterization of Thiomonas arsenivorans sp. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 89(1):99–108
Battaglia-Brunet F, El Achbouni H, Quemeneur M, Hallberg KB, Kelly DP, Joulian C (2011) Proposal that the arsenite-oxidizing organisms Thiomonas cuprina and ‘Thiomonas arsenivorans’ be reclassified as strains of Thiomonas delicata, and emended description of Thiomonas delicata. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(12):2816–2821
Bowell RJ (1994) Sorption of arsenic by iron-oxides and oxyhydroxides in soils. Appl Geochem 9(3):279–286
Brown KG, Ross GL (2002) Arsenic, drinking water, and health: a position paper of the American Council on Science and Health. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 36(2):162–174
Cai L, Liu G, Rensing C, Wang G (2009) Genes involved in arsenic transformation and resistance associated with different levels of arsenic-contaminated soils. BMC Microbiol 9(1):4–13
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17(4):540–552
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Rn Doallo, Posada D (2011) ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 27(8):1164–1165
Drewniak L, Matlakowska R, Sklodowska A (2008) Arsenite and arsenate metabolism of Sinorhizobium sp. M14 living in the extreme environment of the Zloty Stok gold mine. Geomicrobiol J 25(7–8):363–370
Duquesne K, Lieutaud A, Ratouchniak J, Muller D, Lett MC, Bonnefoy V (2008) Arsenite oxidation by a chemoautotrophic moderately acidophilic Thiomonas sp.: from the strain isolation to the gene study. Environ Microbiol 10(1):228–237
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797
Fischer ER, Hansen BT, Nair V, Hoyt FH, Dorward DW (2012) Scanning electron microscopy. Curr Protoc Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471729259.mc02b02s25
Freel KC, Krueger MC, Farasin J, Cl Brochier-Armanet, Vr Barbe, Andrés J, Cholley P-E, Dillies M-As, Jagla B, Koechler S (2015) Adaptation in toxic environments: arsenic genomic islands in the bacterial genus Thiomonas. PLoS ONE 10(9):e0139011
Gao B, Mohan R, Gupta RS (2009) Phylogenomics and protein signatures elucidating the evolutionary relationships among the Gammaproteobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59(2):234–247
Garcia-Dominguez E, Mumford A, Rhine ED, Paschal A, Young LY (2008) Novel autotrophic arsenite-oxidizing bacteria isolated from soil and sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66(2):401–410
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3784–3788
Hamamura N, Macur R, Korf S, Ackerman G, Taylor W, Kozubal M, Reysenbach AL, Inskeep W (2009) Linking microbial oxidation of arsenic with detection and phylogenetic analysis of arsenite oxidase genes in diverse geothermal environments. Environ Microbiol 11(2):421–431
Hamamura N, Itai T, Liu Y, Reysenbach A-L, Damdinsuren N, Inskeep WP (2014) Identification of anaerobic arsenite-oxidizing and arsenate-reducing bacteria associated with an alkaline saline lake in Khovsgol, Mongolia. Environ Microbiol Rep 6(5):476–482
Hughes MF (2002) Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicol Lett 133(1):1–16
Jomova K, Jenisova Z, Feszterova M, Baros S, Liska J, Hudecova D, Rhodes C, Valko M (2011) Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol 31(2):95–107
Kapaj S, Peterson H, Liber K, Bhattacharya P (2006) Human health effects from chronic arsenic poisoning–a review. J Environ Sci Health Part A 41(10):2399–2428
Katoh K, Misawa K, Ki Kuma, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30(14):3059–3066
Leiva ED, Rámila CdP, Vargas IT, Escauriaza CR, Bonilla CA, Pizarro GE, Regan JM, Pasten PA (2014) Natural attenuation process via microbial oxidation of arsenic in a high Andean watershed. Sci Total Environ 466:490–502
Lunau M, Lemke A, Walther K, Martensa-Habbena W, Simon M (2005) An improved method for counting bacteria from sediments and turbid environments by epifluorescence microscopy. Environ Microbiol 7(7):961–968
MathWorks (2016) Bioinformatics toolbox
Meng X, Wang W (1998) Speciation of arsenic by disposable cartridges. In: Book of posters of the third international conference on arsenic exposure and health effects. Society of Environmental Geochemistry and Health Denver, Colorado
Mondal P, Bhowmick S, Chatterjee D, Figoli A, Van der Bruggen B (2013) Remediation of inorganic arsenic in groundwater for safe water supply: a critical assessment of technological solutions. Chemosphere 92(2):157–170
Notredame Cd, Higgins DG, Heringa J (2000) T-Coffee: a novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J Mol Biol 302(1):205–217
Oremland RS, Stolz JF (2003) The ecology of arsenic. Science 300(5621):939–944
Paul D, Poddar S, Sar P (2014) Characterization of arsenite-oxidizing bacteria isolated from arsenic-contaminated groundwater of West Bengal. J Environ Sci Health Part A 49(13):1481–1492
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14(9):817–818
Quemeneur M, Heinrich-Salmeron A, Muller D, Livremont D, Jauzein M, Bertin PN, Garrido F, Joulian C (2008) Diversity surveys and evolutionary relationships of aoxB genes in aerobic arsenite-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(14):4567–4573
Rhine ED, Phelps CD, Young L (2006) Anaerobic arsenite oxidation by novel denitrifying isolates. Environ Microbiol 8(5):899–908
Rhine ED, Onesios KM, Serfes ME, Reinfelder JR, Young L (2008) Arsenic transformation and mobilization from minerals by the arsenite oxidizing strain WAO. Environ Sci Technol 42(5):1423–1429
Rodríguez-Freire L, Sun W, Sierra-Alvarez R, Field JA (2012) Flexible bacterial strains that oxidize arsenite in anoxic or aerobic conditions and utilize hydrogen or acetate as alternative electron donors. Biodegradation 23(1):133–143
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19(12):1572–1574
Salmassi TM, Venkateswaren K, Satomi M, Newman DK, Hering JG (2002) Oxidation of arsenite by Agrobacterium albertimagni, AOL15, sp. nov., isolated from Hot Creek, California. Geomicrobiol J 19(1):53–66
Santini JM, Sly LI, Schnagl RD, Macy JM (2000) A new chemolithoautotrophic arsenite-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a gold mine: phylogenetic, physiological, and preliminary biochemical studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(1):92–97
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17(5):517–568
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30(9):1312–1313
Taly J-F, Magis C, Bussotti G, Chang J-M, Di Tommaso P, Erb I, Espinosa-Carrasco J, Kemena C, Notredame C (2011) Using the T-Coffee package to build multiple sequence alignments of protein, RNA, DNA sequences and 3D structures. Nat Protoc 6(11):1669–1682
Valenzuela C, Campos V, Yañez J, Zaror C, Mondaca M (2009) Isolation of arsenite-oxidizing bacteria from arsenic-enriched sediments from Camarones River, Northern Chile. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82(5):593–596
Welch AH, Westjohn D, Helsel DR, Wanty RB (2000) Arsenic in ground water of the United States: occurrence and geochemistry. Ground Water 38(4):589–604
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Yamamura S, Amachi S (2014) Microbiology of inorganic arsenic: from metabolism to bioremediation. J Biosci Bioeng 118(1):1–9
Zargar K, Hoeft S, Oremland R, Saltikov CW (2010) Identification of a novel arsenite oxidase gene, arxA, in the haloalkaliphilic, arsenite-oxidizing bacterium Alkalilimnicola ehrlichii strain strain MLHE-1. J Bacteriol 192(14):3755–3762
Zargar K, Conrad A, Bernick DL, Lowe TM, Stolc V, Hoeft S, Oremland RS, Stolz J, Saltikov CW (2012) ArxA, a new clade of arsenite oxidase within the DMSO reductase family of molybdenum oxidoreductases. Environ Microbiol 14(7):1635–1645
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by FONDECYT project 1160917 under the Centro de Desarrollo Urbano Sustentable (CEDEUS) CONICYT/FONDAP/15110020. We thanks to Dr. Álvaro Videla from The Department of Mining Engineering at The Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, for ICP-MS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anguita, J.M., Rojas, C., Pastén, P.A. et al. A new aerobic chemolithoautotrophic arsenic oxidizing microorganism isolated from a high Andean watershed. Biodegradation 29, 59–69 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9813-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9813-x