Abstract
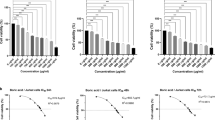
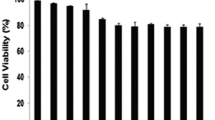
In this study we investigated the effects of boric acid and sodium tetraborate on an acute leukemia cell line and healthy human lymphocytes. We evaluated the effects of boric acid and sodium tetraborate on the HL-60 cell line and healthy human lymphocytes by using the methods of MTT, Neutral Red, AO (flow cytometry) and transmission electron microscope. We found that there were dead cells at a concentration of 500 µM boric acid and sodium tetraborate (50 % and 40 %, respectively). An apoptotic effect was found at a concentration of 1,000 µM concentration in normal lymphocytes and HL-60 (acute leukemia cells) cells (2.5 % and 8.8 % respectively). We observed that boric acid at a concentration of 500 µM caused double nucleus and micronucleus formation in both HL-60 cells and lymphocytes. An expansion in mitochondrial dimension and deformation in cristas also appeared. Our findings suggest that boric acid is more effective than sodium tetraborate on the HL-60, and boric acid in particular showed a cytotoxic effect on HL-60 in comparison to healthy lymphocytes and it also affected the mitochondrial pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bone R, Ashok B (1987) Serine protease mechanism: structure of an inhibitory complex of alfa-lytic protease and a tightly bound peptide boronic acid. Biochemistry 26:7609–7614
Bozola JJ, Russel LD (1999) Electron microscopy, 2 Sub edn. Jones & Bartlett Publishers, Burlington, pp 18–38
Bursh W, Oberhammer F, Schulte-Hermann R (1992) Cell death by apoptosis and its protective role against disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:245–251
Chapin RE, Ku WW (1994) The productive toxicity of Boric Acid. Environ Health Perspect 102:87–91
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bruno S, Del Bino G, Gorczyca W, Hotz MA, Lassota P, Traganos F (1992) Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry 13(8):795–808
Deshayes S, Cabral H, Ishii T, Miura Y, Kobayashi S, Yamashita T, Matsumoto A, Miyahara Y, Nishiyama N, Kataoka K (2013) Phenylboronic acid-installed polymeric micelles for targeting sialylated epitopes in solid tumors. J Am Chem Soc 135:15501–15507
Dibas A, Howard J, Anwar S, Stewart D, Khan A (2000) Borato-1,2 diaminocylohexane platinum (II), a novel anti-tumor drug. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:383–386
Eckhert CD (1998) Boron stimulates embriyonic trout growth. J Nutr 128:2488–2493
Estey E, Döhner H (2006) Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 368:1894–1907
Freshney I (1994) Culture of animal cells. A manual of basic techniques. Wiley, New York, pp 45–195
Gallardo-Williams MT, Maronpot RR, Wine RN, Brunssen SH, Chapin RE (2003) Inhibition of the enzmatic activity of prostate spesific antigen by boric acid and 3-nitrophenyl boronic acid. Prostate 54:44–49
Gallardo-Williams MT, Chapin RE, King PE (2004) Boron supplemantation inhibits the growth and local expresiion of IGF-1 in human prostate adenocarcinoma(LNCaP) tumors in mude mice. Toxicol Pathol 32:73–78
Holsten-Hansten C, Brünner N (1998) MTT cell proliferation assay. In: Celis JE (ed) Cell biology. A laboratory handbook. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 16–18
Horakova K, Sovcıkova A, Seemannova Z, Syrova D, Busanyova K, Drobna Z, Ferencık M (2001) Detection of drug-induced, superoxide-mediated cell damage and its prevention by antioxidants. Free Radic Biol Med 30:650–664
Karp G (1999) Cell and molecular biology. Concepts and experiments. Wiley, New York, pp 123–231
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Murmu N, Mitra S, Das M, Gomes A, Vedasiromoni JR, Ghosh M, Bhattacharya M, Ghosh P, Biswas J, Bhattacharya S, Sur P (2001) Boron compounds against human leukemic cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 20:511–515
Murmu N, Ghosh P, Gomes A, Mitra S, Das M, Besra SE, Majumdar J, Bhattacharya S, Sur P, Vedasiromoni JR (2002) Antineoplastic effect of new boron compounds against leukemic cell lines and cells from leukemic patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 21:351–356
Turkez H, Geyikoğlu F, Tatar A, Keleş S, Ozkan A (2007) Effects of some boron compounds on peripheral human blood. Z Naturforsch C 62: 889–896
Turkez H, Geyikoğlu F, Çolak S (2011) The protective eff ect of boric acid on aluminum-induced hepatotoxicity and genotoxicity in rats. Turk J Biol 35:293–301
Wade TB, Curtis DE (2004) Boric acid inhibits human prostate cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett 216:21–29
Yang W, Gao X, Wang B (2003) Boronic acid compounds as potential pharmaceutical agents. Med Res Rev 23:346–368
Zhang ZF, Winton MI, Rainey C, Eckert CD (2001) Boron is associated with decreased risk of human prostate cancer. Presented at Experimental Biology, Orlando, FL, 31 March–4 April 2001
Acknowledgments
Flow cytometry analyses for the present work were carried out at the Department of Hematology, School of Medicine, Eskişehir Osmangazi University, Eskişehir. The authors gratefully thank Dr. Ayhan Bilir, Department of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey. The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canturk, Z., Tunali, Y., Korkmaz, S. et al. Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of boron compounds on leukemia cell line. Cytotechnology 68, 87–93 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9755-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9755-7