Summary
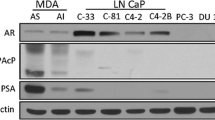
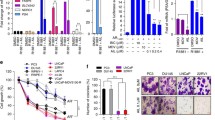
Backgrounds Since most patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) develop resistance to its standard therapy docetaxel, many studies have attempted to identify novel combination treatment to meet the large clinical unmet need. In this study, we examined whether histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) enhanced the effect of docetaxel on AR signaling in CRPC cells harboring AR and its splice variants. Methods HDACIs (vorinostat and CG200745) were tested for their ability to enhance the effects of docetaxel on cell viability and inhibition of AR signaling in CRPC 22Rv1 and VCaP cells by using CellTiter-Glo™ Luminescent cell viability assay, synergy index analysis and Western blotting. The nuclear localization of AR was examined via immunocytochemical staining in 22Rv1 cells and primary tumor cells from a patient with CRPC. Results Combination treatment with HDACIs (vorinostat or CG200745) and docetaxel synergistically inhibited the growth of 22Rv1 and VCaP cells. Consistently, the combination treatment decreased the levels of full-length AR (AR-FL), AR splice variants (AR-Vs), prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins more efficiently compared with docetaxel or vorinostat alone. Moreover, the combination treatment accelerated the acetylation and bundling of tubulin, which significantly inhibited the nuclear accumulation of AR in 22Rv1 cells. The cytoplasmic colocalization of AR-FL and AR-V7 with microtubule bundles increased after combination treatment in primary tumor cells from a patient with CRPC. Conclusions The results suggested that docetaxel, in combination with HDACIs, suppressed the expression and nuclear translocation of AR-FL and AR-Vs and showed synergistic anti-proliferative effect in CRPC cells. This combination therapy may be useful for the treatment of patients with CRPC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grossmann ME, Huang H, Tindall DJ (2001) Androgen receptor signaling in androgen-refractory prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1687–1697
Massard C, Fizazi K (2011) Targeting continued androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17:3876–3883. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-2815
Chen Y, Sawyers CL, Scher HI (2008) Targeting the androgen receptor pathway in prostate cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:440–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2008.07.005
Darshan MS, Loftus MS, Thadani-Mulero M, Levy BP, Escuin D, Zhou XK, Gjyrezi A, Chanel-Vos C, Shen R, Tagawa ST, Bander NH, Nanus DM, Giannakakou P (2011) Taxane-induced blockade to nuclear accumulation of the androgen receptor predicts clinical responses in metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res 71:6019–6029. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-1417
Bissett D, Kaye SB (1993) Taxol and taxotere--current status and future prospects. Eur J Cancer 29a:1228–1231
Yoo J, Park SS, Lee YJ (2008) Pretreatment of docetaxel enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 104:1636–1646. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21729
Marin-Aguilera M, Codony-Servat J, Kalko SG, Fernandez PL, Bermudo R, Buxo E, Ribal MJ, Gascon P, Mellado B (2012) Identification of docetaxel resistance genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 11:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-11-0289
Nadiminty N, Gao AC (2012) Mechanisms of persistent activation of the androgen receptor in CRPC: recent advances and future perspectives. World J Urol 30:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-011-0771-3
Tsao CK, Galsky MD, Small AC, Yee T, Oh WK (2012) Targeting the androgen receptor signalling axis in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). BJU Int 110:1580–1588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11445.x
Scher HI, Sawyers CL (2005) Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol 23:8253–8261. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.03.4777
Wong YN, Ferraldeschi R, Attard G, de Bono J (2014) Evolution of androgen receptor targeted therapy for advanced prostate cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.72
Antonarakis ES, Lu C, Wang H, Luber B, Nakazawa M, Roeser JC, Chen Y, Mohammad TA, Chen Y, Fedor HL, Lotan TL, Zheng Q, De Marzo AM, Isaacs JT, Isaacs WB, Nadal R, Paller CJ, Denmeade SR, Carducci MA, Eisenberger MA, Luo J (2014) AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 371:1028–1038. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1315815
Lu C, Luo J (2013) Decoding the androgen receptor splice variants. Transl Androl Urol 2:178–186. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2013.09.08
Lu J, Van der Steen T, Tindall DJ (2015) Are androgen receptor variants a substitute for the full-length receptor? Nat Rev Urol 12:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2015.13
Antonarakis ES, Lu C, Luber B, Wang H, Chen Y, Nakazawa M, Nadal R, Paller CJ, Denmeade SR, Carducci MA, Eisenberger MA, Luo J (2015) Androgen receptor splice variant 7 and efficacy of taxane chemotherapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. JAMA Oncol 1:582–591. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1341
Guo Z, Yang X, Sun F, Jiang R, Linn DE, Chen H, Chen H, Kong X, Melamed J, Tepper CG, Kung HJ, Brodie AM, Edwards J, Qiu Y (2009) A novel androgen receptor splice variant is up-regulated during prostate cancer progression and promotes androgen depletion-resistant growth. Cancer Res 69:2305–2313. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-3795
Hu R, Dunn TA, Wei S, Isharwal S, Veltri RW, Humphreys E, Han M, Partin AW, Vessella RL, Isaacs WB, Bova GS, Luo J (2009) Ligand-independent androgen receptor variants derived from splicing of cryptic exons signify hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res 69:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-2764
Hu R, Lu C, Mostaghel EA, Yegnasubramanian S, Gurel M, Tannahill C, Edwards J, Isaacs WB, Nelson PS, Bluemn E, Plymate SR, Luo J (2012) Distinct transcriptional programs mediated by the ligand-dependent full-length androgen receptor and its splice variants in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 72:3457–3462. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-3892
Thadani-Mulero M, Portella L, Sun S, Sung M, Matov A, Vessella RL, Corey E, Nanus DM, Plymate SR, Giannakakou P (2014) Androgen receptor splice variants determine taxane sensitivity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 74:2270–2282. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-13-2876
Arsov C, Winter C, Rabenalt R, Albers P (2012) Current second-line treatment options for patients with castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) resistant to docetaxel. Urol Oncol 30:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.02.001
Olsen EA, Kim YH, Kuzel TM, Pacheco TR, Foss FM, Parker S, Frankel SR, Chen C, Ricker JL, Arduino JM, Duvic M (2007) Phase IIb multicenter trial of vorinostat in patients with persistent, progressive, or treatment refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:3109–3115. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2006.10.2434
Piekarz RL, Frye R, Turner M, Wright JJ, Allen SL, Kirschbaum MH, Zain J, Prince HM, Leonard JP, Geskin LJ, Reeder C, Joske D, Figg WD, Gardner ER, Steinberg SM, Jaffe ES, Stetler-Stevenson M, Lade S, Fojo AT, Bates SE (2009) Phase II multi-institutional trial of the histone deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin as monotherapy for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 27:5410–5417. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2008.21.6150
Minucci S, Pelicci PG (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:38–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1779
Hwang JJ, Kim YS, Kim MJ, Kim DE, Jeong IG, Kim CS (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitor potentiates anticancer effect of docetaxel via modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins and tubulin in hormone refractory prostate cancer cells. J Urol 184:2557–2564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.07.035
Hwang JJ, Kim YS, Kim T, Kim MJ, Jeong IG, Lee JH, Choi J, Jang S, Ro S, Kim CS (2012) A novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, CG200745, potentiates anticancer effect of docetaxel in prostate cancer via decreasing Mcl-1 and Bcl-XL. Investig New Drugs 30:1434–1442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9718-1
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzym Regul 22:27–55
Lavery DN, Bevan CL (2011) Androgen receptor signalling in prostate cancer: the functional consequences of acetylation. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:862125. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/862125
Dehm SM, Tindall DJ (2011) Alternatively spliced androgen receptor variants. Endocr Relat Cancer 18:R183–R196. https://doi.org/10.1530/erc-11-0141
van Soest RJ, van Royen ME, de Morree ES, Moll JM, Teubel W, Wiemer EA, Mathijssen RH, de Wit Rvan Weerden WM (2013) Cross-resistance between taxanes and new hormonal agents abiraterone and enzalutamide may affect drug sequence choices in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer 49:3821–3830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2013.09.026
Zhu ML, Horbinski CM, Garzotto M, Qian DZ, Beer TM, Kyprianou N (2010) Tubulin-targeting chemotherapy impairs androgen receptor activity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 70:7992–8002. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-10-0585
Kaushik D, Vashistha V, Isharwal S, Sediqe SA, Lin MF (2015) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer: molecular mechanism of action and recent clinical trials. Ther Adv Urol 7:388–395. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756287215597637
Bradley D, Rathkopf D, Dunn R, Stadler WM, Liu G, Smith DC, Pili R, Zwiebel J, Scher H, Hussain M (2009) Vorinostat in advanced prostate cancer patients progressing on prior chemotherapy (National Cancer Institute Trial 6862): trial results and interleukin-6 analysis: a study by the Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Clinical Trial Consortium and University of Chicago Phase 2 Consortium. Cancer 115:5541–5549. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24597
Rathkopf D, Wong BY, Ross RW, Anand A, Tanaka E, Woo MM, Hu J, Dzik-Jurasz A, Yang W, Scher HI (2010) A phase I study of oral panobinostat alone and in combination with docetaxel in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1289-x
Rathkopf DE, Picus J, Hussain A, Ellard S, Chi KN, Nydam T, Allen-Freda E, Mishra KK, Porro MG, Scher HI, Wilding G (2013) A phase 2 study of intravenous panobinostat in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2224-8
List HJ, Smith CL, Rodriguez O, Danielsen M, Riegel AT (1999) Inhibition of histone deacetylation augments dihydrotestosterone induction of androgen receptor levels: an explanation for trichostatin A effects on androgen-induced chromatin remodeling and transcription of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Exp Cell Res 252:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1999.4638
Welsbie DS, Xu J, Chen Y, Borsu L, Scher HI, Rosen N, Sawyers CL (2009) Histone deacetylases are required for androgen receptor function in hormone-sensitive and castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 69:958–966. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-2216
Kuroda K, Liu H, Kim S, Guo M, Navarro V, Bander NH (2009) Docetaxel down-regulates the expression of androgen receptor and prostate-specific antigen but not prostate-specific membrane antigen in prostate cancer cell lines: implications for PSA surrogacy. Prostate 69:1579–1585. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.21004
Chan SC, Dehm SM (2014) Constitutive activity of the androgen receptor. Adv Pharmacol 70:327–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-417197-8.00011-0
Seruga B, Ocana A, Tannock IF (2011) Drug resistance in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.136
Dehm SM, Schmidt LJ, Heemers HV, Vessella RL, Tindall DJ (2008) Splicing of a novel androgen receptor exon generates a constitutively active androgen receptor that mediates prostate cancer therapy resistance. Cancer Res 68:5469–5477. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-0594
Suzuki J, Chen YY, Scott GK, Devries S, Chin K, Benz CC, Waldman FM, Hwang ES (2009) Protein acetylation and histone deacetylase expression associated with malignant breast cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 15:3163–3171. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-08-2319
Lee HS, Park SB, Kim SA, Kwon SK, Cha H, Lee DY, Ro S, Cho JM, Song SY (2017) A novel HDAC inhibitor, CG200745, inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and overcomes gemcitabine resistance. Sci Rep 7:41615. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41615
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This research was approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB) in Asan Medical Center (#2015-0175). Eighty patient samples were collected and processed immediately after transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Written informed consent was obtained according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the T2B Infrastructure Center for Advancing Cancer Therapeutics (HI15C0972) of the Korea Ministry of Health and Welfare and the Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center (2016-450).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.E., Kim, HG., Kim, D.E. et al. Combination treatment with docetaxel and histone deacetylase inhibitors downregulates androgen receptor signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Invest New Drugs 36, 195–205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0529-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0529-x