Abstract
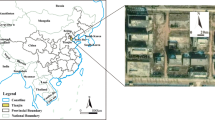
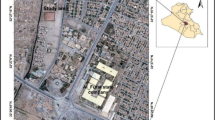
Precise delineation of contaminant plume distribution is essential for effective remediation of contaminated sites. Traditional in situ investigation methods like direct-push (DP) sampling are accurate, but are usually intrusive and costly. Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) method, as a non-invasive geophysical technique to map spatiotemporal changes in resistivity of the subsurface, is becoming increasingly popular in environmental science. However, the resolution of ERT for delineation of contaminant plumes still remains controversial. In this study, ERT and DP technique were both conducted at a real inorganic contaminated site. The reliability of the ERT method was validated by the direct comparisons of their investigation results that the resistivity acquired by ERT method is in accordance with the total dissolved solid concentration in groundwater and the overall variation of the total iron content in soil obtained by DP technique. After testifying the applicability of ERT method for contaminant identification, the extension of contaminant plume at the study site was revealed by supplementary ERT surveys conducted subsequently in the surrounding area of the contaminant source zone.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Zeid, N., Bianchini, G., Santarato, G., & Vaccaro, C. (2004). Geochemical characterisation and geophysical mapping of landfill leachates: the Marozzo canal case study (NE Italy). Environmental Geology, 45(4), 439–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0895-x.
AGI (Advanced Geosciences, Inc.). (2007). Instruction Manual for EarthImager 2D Version 2.2.0 Resistivity and IP Inversion Software: Austin, Texas. Advanced Geosciences Inc, 134 p.
Aizebeokhai, A. P., Olayinka, A. I., & Singh, V. S. (2010). Application of 2D and 3D geoelectrical resistivity imaging for engineering site investigation in a crystalline basement terrain, southwestern Nigeria. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61(7), 1481–1492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0464-z.
Akpan, A. E., Ebong, E. D., & Emeka, C. N. (2015). Exploratory assessment of groundwater vulnerability to pollution in Abi, southeastern Nigeria, using geophysical and geological techniques. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 187(4), 4380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4380-2.
Bernard, J. (2003). Short note on the depth of investigation of electrical methods. http://www.iris-instruments.com/Pdf_file/Resistivity_Imaging/methods_depth_investigation.pdf. Accessed 26 Feb 2018.
Bichet, V., Grisey, E., & Aleya, L. (2016). Spatial characterization of leachate plume using electrical resistivity tomography in a landfill composed of old and new cells (Belfort, France). Engineering Geology, 211, 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.06.026.
Binley, A., & Kemna, A. (2005). DC resistivity and induced polarization methods. Hydrogeophysics, 50, 129–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3102-5_5.
Binley, A. (2015). Tools and techniques: electrical methods A2—Schubert, Gerald, treatise on geophysics (second ed.pp. 233–259). Oxford: Elsevier.
Cardarelli, E., & Di, F. G. (2009). Electrical resistivity and induced polarization tomography in identifying the plume of chlorinated hydrocarbons in sedimentary formation: a case study in rho (Milan—Italy). Waste Management & Research the Journal of the International Solid Wastes & Public Cleansing Association Iswa, 27(6), 595–602. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X09102524.
Cassiani, G., Binley, A., Kemna, A., Wehrer, M., Orozco, A. F., Deiana, R., Boaga, J., Rossi, M., Dietrich, P., & Werban, U. (2014). Noninvasive characterization of the Trecate (Italy) crude-oil contaminated site: links between contamination and geophysical signals. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(15), 8914–8931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2494-7.
China Geological Survey. (2014). Geological survey and evaluation standards for Soil and Groundwater in contaminated sites (DD 2014-06). http://www.cgs.gov.cn/upload/201501/20150105/20150327112909776.pdf. Accessed 26 Feb 2018.
Dahlin, T., Bernstone, C., & Loke, M. H. (2002). A 3-D resistivity investigation of a contaminated site at Lernacken, Sweden. Geophysics, 67(6), 1692–1700. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1527070.
Dahlin, T., & Loke, M. H. (1998). Resolution of 2D Wenner resistivity imaging as assessed by numerical modeling. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 38(4), 237–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9851(97)00030-X.
Dahlin, T., & Zhou, B. (2004). A numerical comparison of 2D resistivity imaging with 10 electrode arrays. Geophysical Prospecting, 52, 379–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2478.2004.00423.x.
Dietrich, P., & Leven, C. (2006). Direct push-technologies. In: Kirsch, J. (Ed.), Ground-water Geophysics. Springer, Berlin, 321–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88405-7_12.
Dietrich, P., Butler Jr., J. J., & Faiss, K. (2008). A rapid method for hydraulic profiling in unconsolidated formations. Groundwater, 46(2), 323–328. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00377.x.
Griffin, T. W., & Watson, K. W. (2002). A comparison of field techniques for confirming dense nonaqueous phase liquids. Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, 22(2), 48–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.2002.tb00312.x.
Grimm, R. E., Olhoeft, G. R., Mckinley, K., Rossabi, J., & Riha, B. (2005). Nonlinear complex-resistivity survey for DNAPL at the savannah river site A-014 outfall. Journal of Environmental & Engineering Geophysics, 10(4), 351–364. https://doi.org/10.2113/JEEG10.4.351.
Halihan, T., Albano, J., Comfort, S. D., & Zlotnik, V. A. (2012). Electrical resistivity imaging of a permanganate injection during in situ treatment of RDX-contaminated groundwater. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation, 32(1), 43–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.2011.01361.x.
Hildenbrand, Z. L., Carlton, D. D., Fontenot, B. E., Meik, J. M., Walton, J. L., Thacker, J. B., Korlie, S., Shelor, C. P., Kadjo, A. F., & Clark, A. (2016). Temporal variation in groundwater quality in the Permian Basin of Texas, a region of increasing unconventional oil and gas development. Science of the Total Environment, 562, 906–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.144.
Johansson, S., Fiandaca, G., & Dahlin, T. (2014). Field application of resistivity and spectral time domain IP to investigate geoelectrical signatures of free-phase PCE. In Near Surface Geoscience 2014-20th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.20142049.
Labrecque, D. J., Miletto, M., Daily, W., Ramirez, A., & Owen, E. (1996). The effects of noise on Occam’s inversion of resistivity tomography data. Geophysics, 61(2), 538–548. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1443980.
Lee, G.F., & Jones, L.A. (1995). Total dissolved solids and groundwater quality protection. Artificial Recharge of Ground Water, II, Proc. International Symposium on Artificial Recharge of Ground Water. New York: American Society of Civil Engineers, 612–618.
Leven, C., Weiß, H., Vienken, T., & Dietrich, P. (2011). Direct-push-technologien—effiziente untersuchungsmethoden für die untergrunderkundung. Grundwasser, 16(4), 221–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00767-011-0175-8.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313(1), 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00683-6.
Loke, M. H., & Dahlin, T. (2002). A comparison of the Gauss–Newton and quasi-Newton methods in resistivity imaging inversion. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 49(3), 149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9851(01)00106-9.
Maurya, P. K., Rønde, V. K., Fiandaca, G., Balbarini, N., Auken, E., Bjerg, P. L., & Christiansen, A. V. (2017). Detailed landfill leachate plume mapping using 2D and 3D electrical resistivity tomography—with correlation to ionic strength measured in screens. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 138, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2017.01.019.
Mccall, W., Nielsen, D. M., Farrington, S. P., & Christy, T. M. (2006). Use of direct-push technologies in environmental site characterization and ground-water monitoring. In practical handbook of environmental site characterization and ground-water monitoring (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
McCall, W., Christy, T. M., Christopherson, T., & Issacs, H. (2009). Application of direct push methods to investigate uranium distribution in an alluvial aquifer. Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, 29 (4), 65-76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.2009.01258.x
Ministry of Land and Resources of China. (2016). Standard for groundwater quality, DZ/T 0290-2015. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
Nguyen, F., Kemna, A., Antonsson, A., Engesgaard, P., Kuras, O., Ogilvy, R., Gisbert, J., Jorreto, S., & Pulido, B. A. (2009). Characterization of seawater intrusion using 2D electrical imaging. Near Surface Geophysics, 7(1303), 377–390. https://doi.org/10.3997/1873-0604.2009025.
Pollock, D., & Cirpka, O. A. (2009). Fully coupled hydrogeophysical inversion of synthetic salt tracer experiments. Water Resources Research, 46(7), 2509. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR008575.
Pujari, P. R., Pardhi, P., Muduli, P., Harkare, P., & Nanoti, M. V. (2007). Assessment of pollution near landfill site in Nagpur, India by resistivity imaging and GPR. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 131(1), 3–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9494-0.
Pujari, P. R., & Soni, A. K. (2009). Sea water intrusion studies near Kovaya limestone mine, Saurashtra coast, India. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 154(1–4), 93–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0380-9.
Rein, A., Holm, O., Trapp, S., Hofmann, S. P., Bittens, M., Leven, C., & Dietrich, P. (2015). Comparison of phytoscreening and direct-push-based site investigation at a rural megasite contaminated with chlorinated ethenes. Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, 35(4), 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwmr.12122.
Revil, A., Karaoulis, M., Johnson, T., & Kemna, A. (2012). Review: Some low-frequency electrical methods for subsurface characterization and monitoring in hydrogeology. Hydrogeology Journal, 20(4), 617–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-011-0819-x.
Revil, A., Schmutz, M., & Batzle, M. L. (2011). Influence of oil wettability upon spectral induced polarization of oil-bearing sands. Geophysics, 76(5), A31–A36. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2011-0006.1.
Rosales, R. M., Martínez-Pagan, P., Faz, A., & Cornejo, J. M. (2012). Environmental monitoring using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) in the subsoil of three former petrol stations in SE of Spain. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223(7), 3757–3773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1146-0.
Rubin, Y. & Hubbard, S.S. (2005). Hydrogeophysics. Dordrecht: Springer.
Rucker, D. F., & Fink, J. B. (2007). Inorganic plume delineation using surface high-resolution electrical resistivity at the BC cribs and trenches site, Hanford. Vadose Zone Journal, 39(5), 946–958. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2006.0169.
Sogade, J. A., Scappuzzo, F. S., Vichabian, Y., Shi, W., Rodi, W., Lesmes, D. P., & Morgan, F. D. (2006). Induced-polarization detection and mapping of contaminant plumes. Geophysics, 71(3), B75–B84. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2196873.
Son, Y. (2011). Assessment of concentration in contaminated soil by potentially toxic elements using electrical properties. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 176(1–4), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1562-9.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vijayaraghavan, K., Vasanthavigar, M., Rajivgandhi, R., & Sarma, V. S. (2011). Integrated techniques to identify groundwater vulnerability to pollution in a highly industrialized terrain, Tamilnadu, India. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 182(1–4), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1857-x.
Wang, T. P., Chen, C. C., Tong, L. T., Chang, P. Y., Chen, Y. C., Dong, T. H., Liu, H. C., Lin, C. P., Yang, K. H., & Ho, C. J. (2015). Applying FDEM, ERT and GPR at a site with soil contamination: a case study. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 121, 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2015.07.005.
Wilson, T. J., Randall, R. R., & Acree, S. (2005). Using direct-push tools to map hydrostratigraphy and predict MTBE plume diving. Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, 25(3), 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.2005.00031.x.
Zume, T. J., Aondover, T., & Scott, C. (2006). Subsurface imaging of an abandoned solid waste landfill site in Norman, Oklahoma. Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, 26(2), 62–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.2006.00066.x.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China grants (No. U1503282 and 41672229). The authors would like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions, which significantly improved the quality of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Highlights
• Direct comparison was made between electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and in situ measurements with direct-push technique for mapping an inorganic contaminant plume at an industrial site.
• The effectiveness of ERT method to identify and delineate the inorganic contaminant plumes in the subsurface was validated by covariation of resistivity changes and of total iron content in soil and the total dissolved solid concentration in groundwater.
• The ERT investigation explored that the extension of inorganic contaminant plume was limited due to the low permeability of porous media in this study area.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Q., Deng, Y., Shi, X. et al. Delineation of contaminant plume for an inorganic contaminated site using electrical resistivity tomography: comparison with direct-push technique. Environ Monit Assess 190, 187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6560-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6560-3