Abstract
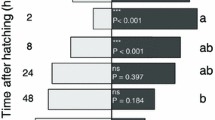
Host prefeeding and acceptance behavior of herbivorous insects may strongly differ depending upon the plant species and previous experience. We examined prefeeding behaviors and acceptance of host and non-host plants by the beetle Phaedon cochleariae in populations with different rearing histories using a camera. Suitable host plants evoked short test biting followed by long feeding durations indicating that these first contacts provide sufficient information to stimulate feeding. In contrast, plants of intermediate quality caused prolonged test biting but feeding duration was rather low. When offered unsuitable plants, beetles showed only rare leaf contacts and test biting, demonstrating that test biting behavior is a useful measure of plant suitability. Rearing history had a minor influence on host plant exploitation behavior.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adati T, Matsuda K (1993) Feeding stimulants for various leaf beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in the leaf surface wax of their host plants. Appl Entomol Zool 28:319–324
Agrawal AA (2001) Ecology—Phenotypic plasticity in the interactions and evolution of species. Science 294:321–326
Badenes-Pérez FR, Reichelt M, Gershenzon J, Heckel DG (2011) Phylloplane location of glucosinolates in Barbarea spp. (Brassicaceae) and misleading assessment of host suitability by a specialist herbivore. New Phytol 189:549–556
Bell WJ (1990) Searching behavior patterns in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 35:447–467
Bengtsson G, Nilsson E, Ryden T, Wiktorsson M (2004) Irregular walks and loops combines in small-scale movement of a soil insect: implications for dispersal biology. J Theor Biol 231:299–306
Bernays EA, Wcislo WT (1994) Sensory capabilities, information processing, and resource specialization. Q Rev Biol 69:187–204
Biere A, Marak HB, van Damme JMM (2004) Plant chemical defense against herbivores and pathogens: generalized defense or trade-offs? Oecologia 140:430–441
Bravo ISJ, Zucoloto FS (1998) Performance and feeding behavior of Ceratitis capitata: comparison of a wild population and a laboratory population. Entomol Exp Appl 87:67–72
del Campo ML, Miles CI, Schroeder FC, Müller C, Booker R, Renwick JA (2001) Host recognition by the tobacco hornworm is mediated by a host plant compound. Nature 411:186–189
Egigu MC, Ibrahim MA, Yahya A, Holopainen JK (2011) Cordeauxia edulis and Rhododendron tomentosum extracts disturb orientation and feeding behavior of Hylobius abietis and Phyllodecta laticollis. Entomol Exp Appl 138:162–174
Eigenbrode SD, Espelie KE (1995) Effects of plant epicuticular lipids on insect herbivores. Annu Rev Entomol 40:171–194
Finch S, Kienegger M (1997) A behavioural study to help clarify how undersowing with clover affects host-plant selection by pest insects of brassica crops. Entomol Exp Appl 84:165–172
Fox CW, Bush ML, Messina FJ (2010) Biotypes of the seed beetle Callosobruchus maculatus have differing effects on the germination and growth of their legume hosts. Agr Forest Entomol 12:353–362
Glendinning JI, Jerud A, Reinherz AT (2007) The hungry caterpillar: an analysis of how carbohydrates stimulate feeding in Manduca sexta. J Exp Biol 210:3054–3067
Guo Q, White RE (2005) Cubic spline regression for the open-circuit potential curves of a lithium-ion battery. J Electrochem Soc 152:A343–A350
Halkier BA, Gershenzon J (2006) Biology and biochemistry of glucosinolates. Annu RevPlant Biol 57:303–333
Henderson AE, Hallett RH, Soroka JJ (2004) Prefeeding behavior of the crucifer flea beetle, Phyllotreta cruciferae, on host and nonhost crucifers. J Insect Behav 17:17–39
Hori M (1998) Repellency of rosemary oil against Myzus persicae in a laboratory and in a screenhouse. J Chem Ecol 24:1425–1432
Hui X, Jin C (2004) Interspecific variation of plant traits associated with resistance to herbivory among four species of Ficus (Moraceae). Ann Bot-London 94:377–384
Isidoro N, Bartlet E, Ziesmann J, Williams IH (1998) Antennal contact chemosensilla in Psylliodes chrysocephala responding to cruciferous allelochemicals. Physiol Entomol 23:131–138
Jourdan H, Barbier R, Bernard J, Ferran A (1995) Antennal sensilla and sexual dimorphism of the adult ladybird beetle Semiadalia undecimnotata Schn. (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae). Int J Insect Morphol 24:307–322
Kühnle A, Müller C (2009) Differing acceptance of familiar and unfamiliar plant species by an oligophagous beetle. Entomol Exp Appl 131:189–199
Kühnle A, Müller C (2011a) Relevance of visual and olfactory cues for host location in the mustard leaf beetle Phaedon cochleariae. Physiol Entomol 36:68–76
Kühnle A, Müller C (2011b) Responses of an oligophagous beetle species to rearing for several generations on alternative host-plant species. Ecol Entomol 36:125–134
Medeiros L, Moreira GRP (2005) Larval feeding behavior of Gratiana spadicea (Klug) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Cassidinae) on its host plant, Solanum sisymbriifolium Lamarck (Solanaceae): interaction with trichomes. Coleopt Bull 59:339–350
Messina FJ (2004) How labile are the egg-laying preferences of seed beetles? Ecol Entomol 29:318–326
Mitchell BK, Low R (1994) The structure of feeding behavior in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). J Insect Behav 7:707–729
Mitchell BK, Itagaki H, Rivet MP (1999) Peripheral and central structures involved in insect gustation. Microsc Res Tech 47:401–415
Müller C, Riederer M (2005) Review: plant surface properties in chemical ecology. J Chem Ecol 31:2621–2651
Müller C, Rosenberger C (2006) Different oviposition behaviour in Chrysomelid beetles: characterisation of the interface between oviposition secretion and the plant surface. Arthropod Struct Dev 35:197–205
Nielsen JK (1978) Host plant discrimination within Cruciferae: feeding responses of four leaf beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) to glucosinolates, cucurbitacins and cardenolides. Entomol Exp Appl 24:41–54
Puttick GM, Bowers MD (1988) Effect of qualitative and quantitative variation in allelochemicals on a generalist insect: iridoid glycosides and the Southern armyworm. J Chem Ecol 14:335–351
Reifenrath K, Müller C (2009) Larval performance of the mustard leaf beetle (Phaedon cochleariae, Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) on white mustard (Sinapis alba) and watercress (Nasturtium officinale) leaves in dependence of plant exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Environ Pollut 157:2053–2060
Reifenrath K, Riederer M, Müller C (2005) Leaf surface wax layers of Brassicaceae lack feeding stimulants for Phaedon cochleariae. Entomol Exp Appl 115:41–50
Renwick JAA, Lopez K (1999) Experience-based food consumption by larvae of Pieris rapae: addiction to glucosinolates? Entomol Exp Appl 91:51–58
Schoonhoven LM, van Loon JJA, Dicke M (2005) Insect-plant biology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Siddiqi MJI, Rana SA, Ismail M, Suhail A (2006) Role of antennal sensilla of soil beetles as food selection in the fields of sugarcane. Pakistan Entomol 28:39–44
Solarz SL, Newman RM (2001) Variation in hostplant preference and performance by the milfoil weevil, Euhrychiopsis lecontei Dietz, exposed to native and exotic watermilfoils. Oecologia 126:66–75
Speyer W, Heikertinger F, von Winning E (1954) Chrysomelidae, Blattkäfer. In: Blunck H (ed) Handbuch der Pflanzenkrankheiten Vol. 5. Paul Parey, Berlin, pp 270–379
Städler E, Reifenrath K (2009) Glucosinolates on the leaf surface perceived by insect herbivores: review of ambiguous results and new investigations. Phytochem Rev 8:207–225
Tanton MT (1962) The effect of leaf “toughness” on the feeding of larvae of the mustard beetle Phaedon cochleariae Fab. Entomol Exp Appl 5:74–78
Travers-Martin N, Müller C (2008) Matching plant defense syndroms with performance and preference of a specialist herbivore. Funct Ecol 22:1033–1043
Traw MB, Dawson TE (2002) Reduced performance of two specialist herbivores (Lepidoptera: Pieridae, Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on new leaves of damaged black mustard plants. Environ Entomol 31:714–722
Tucić N, Milanović D, Mikuljanac S (1995) Laboratory evolution of host plant utilization in the bean weevil (Acanthoscelides obtectus). Genet Sel Evol 27:491–502
Valverde PL, Fornoni J, Nunez-Farfan J (2001) Defensive role of leaf trichomes in resistance to herbivorous insects in Datura stramonium. J Evol Biol 14:424–432
Via S (1990) Ecological genetics and host adaptation in herbivorous insects—the experimental study of evolution in natural and agricultural systems. Annu Rev Entomol 35:421–446
Via S (1991) Specialized host plant performance of pea aphid clones is not altered by experience. Ecology 72:1420–1427
Wood SN (2003) Thin-plate regression splines. J Roy Stat Soc B 65:95–114
Wood SN (2011) Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J Roy Stat Soc B 73:3–36
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the gardeners of Bielefeld University and Helge Landskron for plant cultivation and insect breeding. We thank Ann-Kathrin Höwing and Stefanie Bukovec for help with the video analyses. This work was funded by the grant MU 1829/3-1 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kühnle, A., Müller, C. Prefeeding and Acceptance Behavior of an Oligophagous Beetle is Dependent on Plant Suitability and Rearing History. J Insect Behav 25, 155–165 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-011-9284-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-011-9284-6