Abstract
Purpose
To assess radiation-induced cholecystitis in cases of cystic artery origin nearby the treatment zone for transarterial radioembolization (TARE) treatment.
Materials and methods
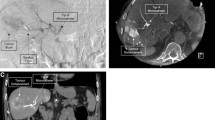
Patients with primary or secondary malignant liver tumors treated with TARE, in whom cystic artery was located in the surrounding area of the treatment zone on 99m-technetium-MAA angiograms, were included in this study. Whole liver dose, tumor dose and healthy injected liver dose, lung dose and if applicable the gallbladder dose were all calculated by using the Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD) formula from SPECT–CT images. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of the gallbladder was performed on SPECT–CT. The observed adverse events were classified according to the National Cancer Institute’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0).
Results
A total of 34 TARE procedures from 29 patients (18 men and 11 women), with a mean age of 65 ± 13.3 years meeting the inclusion criteria, were involved in the current study. The mean tumor dose, healthy injected liver dose, healthy whole liver dose and gallbladder dose were 204.9 ± 66.8 Gy, 70.5 ± 15.7 Gy, 31.1 ± 12.7 Gy and 96.4 ± 53.4 Gy, respectively. The mean follow-up period was 14 ± 5.2 months. Qualitative assessment revealed gallbladder radioactivity on SPECT–CT in 11 (32.3%) patients with six mild and five moderate–severe radioactivities. There were no detected grade 2 or 3 adverse events.
Conclusion
TARE is safely performed without cystic artery embolization when its origin is close to the treatment area.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jakobs TF, Hoffmann RT, Dehm K, Trumm C, Stemmler HJ, Tatsch K et al (2008) Hepatic Yttrium-90 radioembolization of chemotherapy-refractory colorectal cancer liver metastases. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:1187–1195
Lewandowski RJ, Geschwind JF, Liapi E, Salem R (2011) Transcatheter intraarterial therapies: rationale and overview. Radiology 259:641–657
Murthy R, Xiong H, Nunez R, Cohen AC, Barron B, Szklaruk J et al (2005) Yttrium 90 resin microspheres for the treatment of unresectable colorectal hepatic metastases after failure of multiple chemotherapy regimens: preliminary results. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:937–945
Lewandowski RJ, Salem R (2006) Yttrium-90 radioembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic disease to the liver. Semin Intervent Radiol 23:64–72
Borggreve AS, Landman A, Vissers CMJ, De Jong CD, Lam M, Monninkhof EM et al (2016) Radioembolization: is prophylactic embolization of hepaticoenteric arteries necessary? A systematic review. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 39:696–704
Riaz A, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik LM, Mulcahy MF, Sato KT, Ryu RK et al (2009) Complications following radioembolization with Yttrium-90 microspheres: a comprehensive literature review. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:1121–1130 (quiz 31)
Peterson JL, Vallow LA, Johnson DW, Heckman MG, Diehl NN, Smith AA et al (2013) Complications after 90Y microsphere radioembolization for unresectable hepatic tumors: an evaluation of 112 patients. Brachytherapy 12:573–579
Atassi B, Bangash AK, Lewandowski RJ, Ibrahim S, Kulik L, Mulcahy MF et al (2008) Biliary sequelae following radioembolization with Yttrium-90 microspheres. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:691–697
Lauenstein TC, Heusner TA, Hamami M, Ertle J, Schlaak JF, Gerken G et al (2011) Radioembolization of hepatic tumors: flow redistribution after the occlusion of intrahepatic arteries. Rofo 183:1058–1064
Lewandowski RJ, Sato KT, Atassi B, Ryu RK, Nemcek AA Jr, Kulik L et al (2007) Radioembolization with 90Y microspheres: angiographic and technical considerations. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 30:571–592
Ahmadzadehfar H, Sabet A, Biermann K, Muckle M, Brockmann H, Kuhl C et al (2010) The significance of 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT liver perfusion imaging in treatment planning for 90Y-microsphere selective internal radiation treatment. J Nucl Med 51:1206–1212
Lenoir L, Edeline J, Rolland Y, Pracht M, Raoul JL, Ardisson V et al (2012) Usefulness and pitfalls of MAA SPECT/CT in identifying digestive extrahepatic uptake when planning liver radioembolization. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:872–880
Hamami ME, Poeppel TD, Muller S, Heusner T, Bockisch A, Hilgard P et al (2009) SPECT/CT with 99mTc-MAA in radioembolization with 90Y microspheres in patients with hepatocellular cancer. J Nucl Med 50:688–692
Schelhorn J, Theysohn J, Ertle J, Schlaak JF, Mueller S, Bockisch A et al (2014) Selective internal radiation therapy of hepatic tumours: is coiling of the gastroduodenal artery always beneficial? Clin Radiol 69:e216–e222
Petroziello MF, McCann JW, Gonsalves CF, Eschelman DJ, Anne PR, Sato T et al (2011) Side-branch embolization before 90Y radioembolization: rate of recanalization and new collateral development. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:W169–W174
Abdelmaksoud MH, Hwang GL, Louie JD, Kothary N, Hofmann LV, Kuo WT et al (2010) Development of new hepaticoenteric collateral pathways after hepatic arterial skeletonization in preparation for Yttrium-90 radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:1385–1395
Hamoui N, Minocha J, Memon K, Sato K, Ryu R, Salem R et al (2013) Prophylactic embolization of the gastroduodenal and right gastric arteries is not routinely necessary before radioembolization with glass microspheres. J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:1743–1745
Theysohn JM, Muller S, Schlaak JF, Ertle J, Schlosser TW, Bockisch A et al (2013) Selective internal radiotherapy (SIRT) of hepatic tumors: how to deal with the cystic artery. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 36:1015–1022
Boas FE, Bodei L, Sofocleous CT (2017) Radioembolization of colorectal liver metastases: indications, technique, and outcomes. J Nucl Med 58:104S–111S
https://cstep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_8.5x11.pdf. Accessed 27 Nov 2017.
Molmenti EP, Pinto PA, Klein J, Klein AS (2003) Normal and variant arterial supply of the liver and gallbladder. Pediatr Transpl 7:80–82
Mlakar B, Gadzijev EM, Ravnik D, Hribernik M (2003) Anatomical variations of the cystic artery. Eur J Morphol 41:31–34
Sangro B, Bilbao JI, Boan J, Martinez-Cuesta A, Benito A, Rodriguez J et al (2006) Radioembolization using 90Y-resin microspheres for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66:792–800
Garin E, Rolland Y, Boucher E, Ardisson V, Laffont S, Boudjema K et al (2010) First experience of hepatic radioembolization using microspheres labelled with Yttrium-90 (TheraSphere): practical aspects concerning its implementation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:453–461
Padia SA, Lewandowski RJ, Johnson GE, Sze DY, Ward TJ, Gaba RC et al (2017) Radioembolization of hepatic malignancies: background, quality improvement guidelines, and future directions. J Vasc Interv Radiol 28:1–15
Powerski M, Busse A, Seidensticker M, Fischbach F, Seidensticker R, Strach K et al (2015) Prophylactic embolization of the cystic artery prior to radioembolization of liver malignancies—an evaluation of necessity. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 38:678–684
McWilliams JP, Kee ST, Loh CT, Lee EW, Liu DM (2011) Prophylactic embolization of the cystic artery before radioembolization: feasibility, safety, and outcomes. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 34:786–792
Prince JF, van den Hoven AF, van den Bosch MA, Elschot M, de Jong HW, Lam MG (2014) Radiation-induced cholecystitis after hepatic radioembolization: do we need to take precautionary measures? J Vasc Interv Radiol 25:1717–1723
Kao YH, Hock Tan AE, Burgmans MC, Irani FG, Khoo LS, Gong Lo RH et al (2012) Image-guided personalized predictive dosimetry by artery-specific SPECT/CT partition modeling for safe and effective 90Y radioembolization. J Nucl Med 53:559–566
van den Hoven AF, Prince JF, Samim M, Arepally A, Zonnenberg BA, Lam MG et al (2014) Posttreatment PET-CT-confirmed intrahepatic radioembolization performed without coil embolization, by using the antireflux surefire infusion system. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 37:523–528
Salem R, Thurston KG (2006) Radioembolization with 90Yttrium microspheres: a state-of-the-art brachytherapy treatment for primary and secondary liver malignancies. Part 1: technical and methodologic considerations. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:1251–1278
Parakh S, Gananadha S, Allen R, Yip D (2016) Cholecystitis after Yttrium-90 resin microsphere radioembolization treatment: clinical and pathologic findings. Asian J Surg 39:144–148
Bester L, Meteling B, Pocock N, Pavlakis N, Chua TC, Saxena A et al (2012) Radioembolization versus standard care of hepatic metastases: comparative retrospective cohort study of survival outcomes and adverse events in salvage patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol 23:96–105
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
This study has obtained IRB approval from Yeditepe University Ethical Committee (IRB approval number: 862), and the need for informed consent was waived.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topcuoglu, O.M., Alan Selcuk, N., Sarikaya, B. et al. Safety of transarterial radioembolization with Yttrium-90 glass microspheres without cystic artery occlusion. Radiol med 124, 575–580 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-018-00984-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-018-00984-9