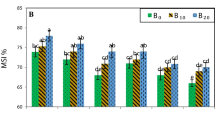
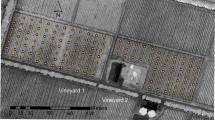
Abstract
In order to improve our knowledge of the mechanical effect of the roots of mixed-plantings on soil reinforcement and slope protection, the influence of roots of a mixed-planting with four herb species (Medicago sativa L., Elymus nutans Griseb., Puccinellia distanx (L.), and Poa pratensis L.) and one shrub species (Caragana korshinskii Kom.) were investigated on the shear strength characteristics of saline loess soil. The root distribution characteristics were assessed via a survey when the plants grew for one year. The effects of the root biomass density, the root mass ratio (RMR) of the fine roots to the coarse roots, the moisture content, and the salt content on the shear strength index of the rooted soil were analyzed via a triaxial compression test, and the mechanism of these effects was discussed. The results indicate that the biomass density decreased linearly with increasing depth. The RMR initially decreased with depth and then increased, exhibiting in a quadratic relationship. The cohesion of the rooted soil increased linearly as the biomass density increased. The cohesion of the rooted soil initially increased with increasing RMR and salt content, and then it decreased. The turning point of the cohesion occurred when the RMR was 0.6 and the salt content was 1.18%. The internal friction angle of the rooted soil initially increased with biomass density and then decreased, and the turning point of the internal friction angle occurred when the biomass density was 0.015 g/cm3. The relationships between the internal friction angle of the rooted soil and the RMR and salt content were exponential incremental and linear subtractive relationship, respectively. Both the cohesion and the internal friction angle of the rooted soil linearly decreased with increasing moisture content.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Bing H, He P (2011) Experimental investigations on the influence of cyclical freezing and thawing on physical and mechanical properties of saline soil. Environ Earth Sci 64(2): 431–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0858-y
Chen SH (2001) Root system of plants in grassland in northern China, Changchun, China. Jilin University Publishing House. p 43, 128, 139, 179. (In Chinese)
Chau NL, Chu LM (2017) Fern cover and the importance of plant traits in reducing erosion on steep soil slopes. Catena 151: 98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.12.016
Fu JT, Hu XS, Li XL, et al. (2019) Influences of soil moisture and salt content on loess shear strength in the Xining Basin, northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J Mt Sci 16(5): 1184–1197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5206-9
Fan ER, Zhang W, Li K, et al. (2001) Engineering properties of loess salted soil and its foundation treating methods. Geotechnical Engineering Technique (1): 27–30. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2001.01.007
Fu J T, Hu X S, Brierley G, et al. (2016) The influence of plant root system architectural properties upon the stability of loess hillslopes, Northeast Qinghai, China. J Mt Sci 13(5): 785–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3275-y
Ghestem M, Veylon G, Bernard A, et al. (2014) Influence of plant root system morphology and architectural traits on soil shear resistance. Plant Soil 377(1–2): 43–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1572-1
Giadrossich F, Schwarz M, Cohen D, et al. (2017) Methods to measure the mechanical behaviour of tree roots: A review. Ecol Eng 109: 256–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.08.032
Hu XS, Mao XQ, Zhu HL, et al. (2011) Vegetation slope protection in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Beijing, China. Geological Publishing House, p 15, 24. (In Chinese)
Ji XL (2013) A roots distribution-based study on the stability of ecological slope. PhD thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, Jiangsu. p 83. (In Chinese)
Ji XD, Cong X, Dai XQ, et al. (2018) Studying the mechanical properties of the soil-root interface using the pullout test method. J Mt Sci 15(4): 882–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-015-3791-4
Li SL, Xu WN, Feng Z, et al. (2007) Study on design method of plant community types in slope ecological restoration. Soil Water Conserv China (12): 53–55. (In Chinese)
Lu XT (2017) Study on ecological slope protection technology in loess area. Master thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, Shanxi. p 23. (In Chinese)
Long H, Sun S, Liu Y, et al. (2018) Surveying fault structures by Geophysical exploration technique on the northwestern margin of Xining Basin. Geophys Geochem Explor 42(2): 241–246. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11720/wtyht.2018.2.03
Luo YD (2010) Investigation of the distribution of saline soil in Qinghai and its unique engineering properties. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 37(4): 116–120. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.04.024
Li RJ (1993) Causes and control measures of secondary saline soil in Huangshui River Basin. Qinghai Environ 3(2): 75–80. (In Chinese)
Li GX (2016) Advanced soil mechanics, Beijing, China. Tsinghua University Press. p 123. (In Chinese)
Lai Y M, Wu D, Zhang M (2017) Crystallization deformation of a saline soil during freezing and thawing processes. Appl Therm Eng 120: 463–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.04.011
Mickovski SB, Bengough AG, Bransby MF, et al. (2007) Material stiffness, branching pattern and soil matric potential affect the pullout resistance of model root systems. Eur J Soil Sci 58(6):1471–1481. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2007.00953.x
Mickovski SB, Stokes A, Beek RV, et al. (2011) Simulation of direct shear tests on rooted and non-rooted soil using finite element analysis. Ecol Eng 37(10): 1523–1532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.06.001
Mao Z, Bourrier F, Stokes A, et al. (2014) Three-dimensional modelling of slope stability in heterogeneous montane forest ecosystems. Ecol Model 273(2): 11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.10.017
Meijer GJ, Bengough AG, Knappett JA, et al. (2018) In situ measurement of root reinforcement using corkscrew extraction method. Can Geotech J 55(10): 1372–1390. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2017-0344
Ng CWW (2016) Atmosphere-plant-soil interactions: theories and mechanisms. Chin J Geotech Eng 39(1):1–46. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201701001
Ni J, Leung AK, Ng CWW (2019) Unsaturated hydraulic properties of vegetated soil under single and mixed planting conditions. Geotechnique 69(6):554–559. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.17.T.044
Sun B, Guo ZT, Yin QZ, et al. (2006) Soluble salts in a Quaternary loess soil sequence near Xining and their environmental implications. Quat Sci 26(4): 649–656. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.04.022
Sun Y (2013) The development characteristics and stability analysis of Xining loess landslide — Take the Xiaoyoushan landslide as example. Master thesis, Changan University, Xi’an, Shanxi. p 1. (In Chinese)
Schwarz M, Preti F, Giadrossich F, et al. (2010a) Quantifying the role of vegetation in slope stability: A case study in Tuscany (Italy). Ecol Eng 36(3): 285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.06.014
Schwarz M, Cohen D, Or D (2010b) Root-soil mechanical interactions during pullout and failure of root bundles. J Geophys Res-Earth Surf 115: F04035. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JF001603.
Stokes A, Douglas GB, Fourcaud T, et al. (2014) Ecological mitigation of hillslope instability: ten key issues facing researchers and practitioners. Plant Soil 377(1–2): 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2044-6
Wu TH, Mckinnell WP, Swanston DN (1979) Strength of treeroots and landslides on Prince of Wales Island, Alaska. Can Geotech J 16(1): 19–33. https://doi.org/10.1139/t79-003
Waldron LJ, Dakessian S (1981) Soil reinforcement by roots: calculation of increased soil shear resistance from root properties. Soil Sci 132(6): 427–435. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-198112000-00007
Wang (2010) The problems of great importance in the project construction of the region of loess-like saline soil in Xining. J Geol Hazards Environ Preserv 21(3): 79–82. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2010.03.015
Wang Y, Du F, Zhou M, et al. (2018) Research on shear strength of root-soil composite in a forest and grass standing site in Northern Shaanxi. Res Soil Water Conserv 25(2): 213–219. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2018.02.031
Wang YH, Zhang X (2011) Analysis on the characteristic and change trend of precipitation in Xi’ning city. Res Soil Water Conserv 18(5): 156–160. (In Chinese)
Yang YH (2006) Study on mechanism of vegetation reinforcing soil and maintaining slope stability in gravelly soil region in Dongchuan Yunnan province. Master thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, Sichuan. P 155. (In Chinese)
Yang F, Liu L (2012) Study on occurrence pattern and trend of drought in east Qinghai Province. Arid Zone Res 29(2): 284–288. (In Chinese)
Yamase K, Tanikawa T, Dannoura M, et al. (2019) Estimating slope stability by lateral root reinforcement in thinned and unthinned stands of Cryptomeria japonica using ground-penetrating radar. Catena 183: 104227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104227
Yan ZX, Cao XH, Zhang LP, et al. (2011) Mechanical mechanism analysis of plant slope protection. Railway Engineering (4): 92–94. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2011.04.030
Zhang XL, Hu XS (2013) Shear characteristics of reinforced soil of herb roots in loess area of Northeast Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Bull Soil Water Conserv 33(4): 185–188. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2013.04.035
Zhou PD, Zhang JY (2003) The engineering technology for slope protection by vegetation, Beijing, China. China Communications Press. p 66,115. (In Chinese)
Zhang CB, Chen LH, Liu YP, et al. (2010) Triaxial compression test of soil-root composites to evaluate influence of roots on soil shear strength. Ecol Eng 36(1): 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.09.005
Zhou YY (2010) Study on Mechanism of Soil Reinforcement by Roots and Slope Protection Technology. PhD thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, Hubei. p 58, 99. (In Chinese)
Zhao QY, Zhang AJ, Wang YG, et al. (2019) Effects of soluble content on strength of original unsaturated Ili loess. J Northwest A F Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 47(4): 146–154. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2019.04.018
Acknowledgments
This project was financially supported by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (STEP) program (Grant No. 2019QZKK0905), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42002283, 41572306, 42041006 and 42062019), the Project of the Qinghai Science & Technology Department (Grant Nos. 2020-ZJ-906 and 2014-ZJ-906), the Key Discipline Construction Project for Geological Resources and Geological Engineering of Qinghai University (Grant No. 41250103), and the Ministry of Education’s ‘Innovative Team Development Scheme’ (IRT_17R62). We thank all of the anonymous reviewers for providing helpful comments for the improvement of the manuscript. We also thank ACCDON for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Yb., Hu, Xs., Yu, Dm. et al. Influence of the roots of mixed-planting species on the shear strength of saline loess soil. J. Mt. Sci. 18, 806–818 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6169-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6169-1