Abstract
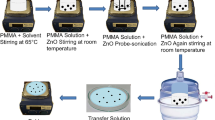
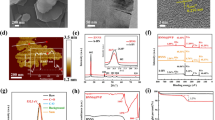
A novel two-phase composite film is prepared by the solvent casting method employing poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) as polymer matrix and bismuth ferrite (BFO) as ceramic filler. The surfaces of BFO are functionalized by proper hydroxylating agents to activate their chemical nature. The structural analysis of the composite films confirms that the composites made up of functionalized BFO (BFO-OH) have a distorted rhombohedral structure. The morphological analysis shows that BFO-OH particles are equally distributed over the polymer matrix. The -OH functionality of BFO-OH is confirmed by FTIR. The dielectric and electrical studies at a frequency range from 100 Hz to 1 MHz reveal that PMMA-(BFO-OH) composites have enhanced dielectric constant as well as electrical conductivities, much higher than that of unmodified composites. According to the ferroelectric measurement result, the hydroxylated composite film shows a superior ferroelectric behavior than that of the unmodified one, with a remanent polarization (2Pr) of 2.764 μC/cm2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yuan J K, Li W L, Yao S H, et al. High dielectric permittivity and low percolation threshold in polymer composites based on SiCcarbon nanotubes micro/nano hybrid. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(3): 032901
Vishnuvardhan T K, Kulkarni V R, Basavaraja C, et al. Synthesis, characterization and a.c. conductivity of polypyrrole/Y2O3 composites. Bulletin of Materials Science, 2006, 29(1): 77–83
Sava F, Cristescu R, Socol G, et al. Structure of bulk and thin films of poly(methyl methacrilate (PMMA) polymer prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 2002, 4(4): 965–970
Grossiord N, Loos J, Koning C E, et al. Strategies for dispersing carbon nanotubes in highly viscous polymers. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2005, 15(24): 2349–2352
Arbatti M, Shan X, Cheng Z Y, et al. Ceramic–polymer composites with high dielectric constant. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(10): 1369–1372
Stefanescu E A, Tan X, Lin Z, et al. Multifunctional PMMA–ceramic composites as structural dielectrics. Polymer, 2010, 51(24): 5823–5832
Wang H, Xiang F, Li K, et al. Ceramic–polymer Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3/ poly(methyl methacrylate) composites with different type composite structures for electronic technology. Applied Ceramic Technology, 2010, 7(4): 435–443
Khattari Z, Maghrabi M, McNally T, et al. Impedance study of polymethyl methacrylate composites/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (PMMA/MWCNTs). Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2012, 407(4): 759–764
Jung S, Baeg K, Yoon S, et al. Low-voltage-operated top-gate polymer thin-film transistors with high capacitance poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)/poly(methyl methacrylate) dielectrics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(10): 102810
Ahlawat A, Satapathy S, Bhartiya S, et al. BiFeO3/poly(methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite films: A study on magnetic and dielectric properties. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(4): 042902 (3 pages)
Fiebig M, Lottermoser T, Fröhlich D, et al. Observation of coupled magnetic and electric domains. Nature, 2002, 419(6909): 818–820
Loh K J, Chang D. Zinc oxide nanoparticle-polymeric thin films for dynamic strain sensing. Journal of Materials Science, 2011, 46(1): 228–237
Setvín M, Daniel B, Mansfeldova V, et al. Surface preparation of TiO2 anatase (101): Pitfalls and how to avoid them. Surface Science, 2014, 626: 61–67
Beier C W, Cuevas M A, Brutchey R L. Effect of surface modification on the dielectric properties of BaTiO3 nanocrystals. Langmuir, 2010, 26(7): 5067–5071
Kim P, Jones S C, Hotchkiss P J, et al. Phosphonic acid-modified barium titanate polymer nanocomposites with high permittivity and dielectric strength. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(7): 1001–1005
Song Y, Shen Y, Liu H Y, et al. Improving the dielectric constants and breakdown strength of polymer composites: effects of the shape of the BaTiO3 nanoinclusions, surface modification and polymer matrix. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(32): 16491–16498
Chon J, Ye S, Cha K J, et al. High-dielectric sol–gel hybrid materials containing barium titanate nanoparticles. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(19): 5445–5452
Li J, Claude J, Norena-Franco L E, et al. Electrical energy storage in ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites containing surfacefunctionalized BaTiO3 nanoparticles. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(20): 6304–6306
Chu L W, Prakash K N, Tsai M T, et al. Dispersion of nano-sized BaTiO3 powders in nonaqueous suspension with phosphate ester and their applications for MLCC. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2008, 28(6): 1205–1212
Sharma S, Tomar M, Kumar A, et al. Multiferroic properties of BiFeO3/BaTiO3 multilayered thin films. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2014, 448: 125–127
Lee M H, Lee S C, Sung Y S, et al. Improvement of ferroelectric and leakage current properties with Zn–Mn co-doping in BiFeO3 thin films. Ferroelectrics, 2010, 401(1): 186–191
Godara S, Sinha N, Ray G, et al. Combined structural, electrical, magnetic and optical characterization of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by auto-combustion route. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 2014, 2(4): 416–421
Xie L, Huang X, Huang Y, et al. Core@double-shell structured BaTiO3–polymer nanocomposites with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss for energy storage application. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(44): 22525–22537
Paniagua S A, Kim Y, Henry K, et al. Surface-initiated polymerization from barium titanate nanoparticles for hybrid dielectric capacitors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(5): 3477–3482
Bajpai O P, Kamdi J B, Selvakumar M, et al. Effect of surface modification of BiFeO3 on the dielectric, ferroelectric, magneto–dielectric properties of polyvinylacetate/BiFeO3 nanocomposites. Express Polymer Letters, 2014, 8(9): 669–681
Ray D K, Himanshu A K, Sinha T P, et al. Structural and low frequency dielectric studies of conducting polymer nanocomposites. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics, 2007, 45: 692–699
Tripathi S K, Gupta A, Kumari M, et al. Studies on electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of PVdF–HFP–PMMA–NaI polymer blend electrolyte. Bulletin of Materials Science, 2012, 35(6): 969–975
Zhao R, Zhao J, Wang L, et al. Reduced sedimentation of barium titanate nanoparticles in poly(vinylidene fluoride) films during solution casting by surface modification. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2015, 132(42): 42662
Prakash B S, Varma K B R. Dielectric behavior of CCTO/epoxy and Al-CCTO/epoxy composites. Composites Science and Technology, 2007, 67(11–12): 2363–2368
Sengwa R J, Choundhary S, Sankhla S. Dielectric properties of montmorillonite clay filled poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(ethylene oxide) blend nanocomposites. Composites Science and Technology, 2010, 70(11): 1621–1627
Catalan G, Scott J F. Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(24): 2463–2485
Luther G. Dielectric dispersion of ferroelectric triglycine sulphate in the microwave region. Physica Status Solidi A: Applied Research, 1973, 20(1): 227–236
Thakur V K, Tan E J, Lin M F, et al. Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-graft-poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate): a novel material for high energy density capacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(11): 3751–3759
Jayalakshmi M, Balasubramanian K. Simple capacitors to supercapacitors - an overview. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2008, 3: 1196–1217
Rajalakshmi R, Kambhala N, Angappane S, et al. Enhanced magnetic properties of chemical solution deposited BiFeO3 thin film with ZnO buffer layer. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2012, 177(11): 908–912
Ramesh S, Liew C W, Arof A K. Ion conducting corn starch biopolymer electrolytes doped with ionic liquid 1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2011, 357(21): 3654–3660
Park J H, Hwang D K, Lee J, et al. Studies on poly(methyl methacrylate) dielectric layer for field effect transistor: Influence of polymer tacticity. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(7–8): 4041–4044
Gravatt C C, Gross P M. Effect of hydrogen bonding on the electrical conductivity of organic solids. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1967, 46(2): 413
Singh V R, Dixit A, Garg A, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the structure and properties of chemical solution processed multiferroic BiFeO3 thin films. Applied Physics A: Materials Science & Processing, 2008, 90(1): 197–202
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere thanks to Sambalpur University for providing the facilities for research works. We are also thankful to NIT Raipur for providing the facilities of XRD & SEM study and University Grant Commissions (UGC) (F. No: 42-277/2013) (SR), New Delhi, Government of India, for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, M.K., Moharana, S., Behera, B. et al. Surface functionalization of BiFeO3: A pathway for the enhancement of dielectric and electrical properties of poly(methyl methacrylate)–BiFeO3 composite films. Front. Mater. Sci. 11, 82–91 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-017-0364-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-017-0364-1