Abstract
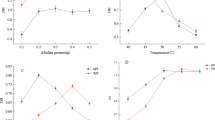
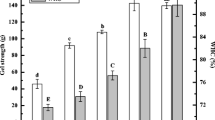
The poor solubility and functionalities of soy protein concentrate (SPC) limits its utilization in meat products. Phosphate-assisted hydrothermal cooking (HTC) was applied to refunctionalize SPC in this work. The resultant soy protein isolate (SPI) was used as an ingredient for improving the gelation of porcine myofibrillar protein (MP) which was induced by microbial transglutaminase (MTGase). The addition of sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP) enhanced the refunctionalization efficiency of HTC and increased the phosphorus content in the obtained SPI. Dynamic rheological analysis indicated that this SPI itself could not form a gel with the help of MTGase. However, the SEM observation revealed that the presence of this SPI strengthened the gel network of MP and made it become denser and more ordered. As a result, the mechanical properties and water holding capacity of the MP gel were significantly improved by this SPI prepared by phosphate-assisted HTC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun XD, Holley RA (2011) Factors influencing gel formation by myofibrillar proteins in muscle foods. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 10:33–51
Hong GP, Chin KB (2010) Effects of microbial transglutaminase and sodium alginate on cold-set gelation of porcine myofibrillar protein with various salt levels. Food Hydrocoll 24:444–451
Ramírez-Suárez JC, Barrera M, Morales OG, Vazquez M (2002) Effect of xanthan and locust bean gums on the gelling of myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll 16:11–16
Sun XD, Arntfield SD (2012) Gelation properties of myofibrillar/pea protein mixtures induced by transglutaminase crosslinking. Food Hydrocoll 27:394–400
Day L (2013) Proteins from land plants-potential resources for human nutrition and food security. Trends Food Sci Tech 32:25–42
Wolf WJ (1975) Lipoxygenase and flavor of soybean protein products. J Agric Food Chem 23:136–141
Das AK, Anjaneyulu ASR, Gadekar YP, Singh RP, Pragati H (2008) Effect of full-fat soy paste and textured soy granules on quality and shelf-life of goat meat nuggets in frozen storage. Meat Sci 80:607–614
Feng J, Xiong YL (2002) Interaction of myofibrillar and preheated soy proteins. J Food Sci 67:2851–2856
Feng J, Xiong YL (2003) Interaction and functionality of mixed myofibrillar and enzyme-hydrolyzed soy proteins. J Food Sci 68:803–809
Liu G, Xiong YL, Butterfield DA (2000) Chemical, physical, and gel-forming properties of oxidized myofibrils and whey- and soy-protein isolates. J Food Sci 65:811–818
Jiang J, Xiong YL (2013) Extreme pH treatments enhance the structure-reinforcement role of soy protein isolate and its emulsions in pork myofibrillar protein gels in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Meat Sci 93:469–476
Wu N, Wang L, Yang X, Yin S, Teng Z, Zheng E (2011) Comparison of flavor volatiles and some functional properties of different soy protein products. J Am Oil Chem Soc 88:1621–1631
Wang C, Johnson LA (2001) Functional properties of hydrothermally cooked soy protein product. J Am Oil Chem Soc 78:189–195
Zheng HG, Yang XQ, Tang CH, Li L, Ahmad I (2008) Preparation of soluble soybean protein aggregates (SSPA) from insoluble soybean protein concentrates (SPC) and its functional properties. Food Res Int 41:154–164
Detienne NA, Wicker L (1999) Sodium chloride and tripolyphosphate effects on physical and quality characteristics of injected pork loins. J Food Sci 64:1042–1047
Folk JE, Cole PW (1965) Structural requirements of specific substrates for guinea pig liver transglutaminase. J Biol Chem 240:2951–2960
Xiong YL (1993) A comparison of the rheological characteristics of different fractions of chicken myofibrillar proteins. J Food Biochem 16:217–227
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177:751–766
Chen PS, Toribara TY Jr, Warner H (1956) Microdetermination of phosphorus. Anal Chem 28:1756–1758
Enomoto H, Li CP, Morizane K, Ibrahim HR, Sugimoto Y, Ohki S, Ohtomo H, Aoki T (2007) Glycation and phosphorylation of β-lactoglobulin by dry-heating: effect on protein structure and some properties. J Agric Food Chem 55:2392–2398
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall OJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Çakır E, Daubert CR, Drake MA, Vinyard CJ, Essick G, Foegeding EA (2012) The effect of microstructure on the sensory perception and textural characteristics of whey protein/κ-carrageenan mixed gels. Food Hydrocoll 26:33–43
Truong VD, Daubert CR (2000) Comparative study of large strain methods for assessing failure characteristics of selected food gels. J Texture Stud 31:335–353
Wu M, Xiong YL, Chen J, Tang X, Zhou G (2009) Rheological and microstructural properties of porcine myofibrillar protein-lipid emulsion composite gels. J Food Sci 74:207–217
Rastogi S, Terry AE, Vinken E (2004) Dissolution of hydrogen-bonded polymers in water: a study of nylon-4,6. Macromolecules 37:8825–8828
Wang H, Wang T, Johnson LA (2006) Mechanism for refunctionalizing heat-denatured soy protein by alkaline hydrothermal cooking. J Am Oil Chem Soc 83:39–45
Guo J, Zhang Y, Yang XQ (2012) A novel enzyme cross-linked gelation method for preparing food globular protein-based transparent hydrogel. Food Hydrocolloid 26:277–285
Sun J, Li X, Xu X, Zhou G (2011) Influence of various levels of flaxseed gum addition on the water-holding capacities of heat-induced porcine myofibrillar protein. J Food Sci 76:C472–C478
Pietrasik Z, Jarmoluk A, Shand PJ (2003) Effect of non-meat proteins on hydration and textural properties of pork meat gels enhanced with microbial transglutaminase. LWT-Food Sci Technol 40:915–920
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2013M530367), the National Natural Science Fund of China (Nos. 31371744 and 31130042) and the Project of National Key Technology Research and Development Program for the 12th Five-year Plan (No. 2012BAD34B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Hu, L., Yang, XQ. et al. Influence of Soy Protein Isolate Prepared by Phosphate-Assisted Hydrothermal Cooking on the Gelation of Myofibrillar Protein. J Am Oil Chem Soc 92, 523–531 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2617-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2617-4