Abstract
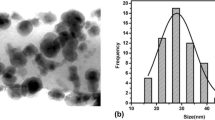
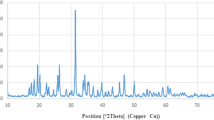
In this study, we synthesized tungsten oxide (WO3) nanoplates, both crystallographic phases and the morphology of the samples were determined by powder x-ray diffraction and the scanning electron microscopy, respectively. The obtained data clarified that, the all prepared WO3·H2O samples were composed of large quantity of nanoplates. The cytotoxicity patterns of nanoplates were checked on both normal and cancer mammalian cell lines. Both nanoplates cytotoxicity did not exceed the 50 % inhibitory concentration (IC50) on the all normal tested cells even by using concentrations up to 1 mg/ml. In addition, orthorhombic tungsten oxide nanoplate was more potent against both Caco2 and Hela cells by showing inhibition percentages in cellular viability 64.749 and 72.27, respectively, and with cancer selectivity index reached 3.2 and 2.6 on both colon and cervix cancer, respectively. The anticancer effects of nanoplates were translated to alteration in both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic genes expressions. Tungsten oxide nanoplates down regulated the expression of B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7) genes. In addition, orthorhombic tungsten oxide nanoplates showed more potentiation in IL2 and IL8 induction (40.43 pg/ml) and upregulation of TNF-α gene expression but with lower folds than Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induction.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajagopal, S., Nataraj, D., Mangalaraj, D., Djaoued, Y., Robichaud, J., & Khyzhun, O. Y. (2009). Nanoscale Res Letter, 4, 1335–1342. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1878535215001379#b0155.
Elnouby, M., Kuruma, K., Nakamura, E., Abe, H., Suzuki, Y., & Naito, M. (2013). Synthesis of WO3· 0.33 H2O nanoneedles by hydrothermal treatment of ion exchanged precursor. Journal of Flux Growth 62–65.
Lu, X., Liu, X., Zhang, W., Wang, C., & Wei, Y. (2006). Large-scale synthesis of tungsten oxide nanofibers by electrospinning. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 298(2), 996–999. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212670814000323#bib0050.
Elnouby, M., Kuruma, K., Nakamura, E., Abe, H., Suzuki, Y., & Naito, M. (2013). Facile synthesis of WO3 · H2O square nanoplates via a mild aging of ion exchanged precursor. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 121, 907–911. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259441526_Facile_synthesis_of_WO3H2O_square_nanoplates_via_a_mild_aging_of_ion-exchanged_precursor.
Xiao, W., Liu, W., Mao, X., Zhu, H., & Wang, D. (2013). Na2SO4-assisted synthesis of hexagonal-phase WO3 nanosheet assemblies with applicable electrochromic and adsorption properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry, A 1, 1261–1269. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2013/TA/c2ta00545j#!divAbstract.
Soliman, H. M. A., Kashyout, A. B., El Nouby, M. S., & Abosehly, A. M. (2012). Effect of hydrogen peroxide and oxalic acid on electrochromic nanostructured tungsten oxide thin films. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 7, 258–271. http://connection.ebscohost.com/c/articles/71772821/effect-hydrogen-peroxide-oxalic-acid-electrochromic-nanostructured-tungsten-oxide-thin-films.
Soliman, H. M. A., Kashyout, A. B., El Nouby, M. S., & Abosehly, A. M. (2010). Preparation and characterizations of tungsten oxide electrochromic nanomaterials. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 21, 1313–1321. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10854-010-0068-0#page-1.
Kim, M. C., Cui, F. J., & Kim, Y. (2013). Hydrogen peroxide promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and stemness in human malignant mesothelioma cells. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 14, 3625–30. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23886156.
Zhao, J., Bowman, L., & Magaye, R. (2013). Apoptosis induced by tungsten carbide-cobalt nanoparticles in JB6 cells involves ROS generation through both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways. International Journal of Oncology, 42, 1349–59. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23417053.
Ivankovic, S., Music, S., Gotic, M., & Ljubes, M. (2006). Cytotoxicity of nanosize V2O5 particles to selected fibroblast and tumor cells. Toxicology In Vitro, 20,286. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S088723330500158X.
Johnson, M. K., Rees, D. C., & Adams, M. W. W. (1996). Tungstoenzymes. Chemical Reviews, 96, 2817. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11848842.
Louie, A. Y., & Meade, J. J. (1999). Metal complexes as enzyme inhibitors. Chemical Review, 99, 2711. http://serials.unibo.it/cgi-ser/start/en/spogli/df-s.tcl?prog_art=6525492&language=ENGLISH&view=articoli.
Mosmann, T. (1983). Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Journal of Immunological Methods, 65, 55–63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6606682.
Borenfreund, E., & Puerner, J. A. (1985). Toxicity determined in vitro by morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicology Letters, 24, 119–124. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Toxicity+determined+in+vitro+by+morphological+alterations+and+neutral+red+absorption.
Koch, A., Tamez, P., Pezzuto, J., & Soejarto, D. (2005). Evaluation of plants used for antimalarial treatment by the Maasai of Kenya. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 3;101(1–3), 95–9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15878245/.
Lohr, H. F., Goergen, B., Meyer, Z. M., Buschenfelde, K. H., & Gerken, G. (1995). HCV replication in mononuclear cells stimulates anti-HCV-secreting B cells and reflects nonresponsiveness. Journal of Medical Virology, 46(4), 314–20. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=HCV+replication+in+mononuclear+cells+stimulates+anti-HCV-secreting+B+cells+and+reflects+nonresponsiveness.
Kim, S. J., Hwang, I. S., Choi, J. K., & Lee, J. H. (2011). Color-tunable electrophosphorescent device fabricated by a photo-bleaching method. Thin Solid Films, 519, 2020–2024. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040609011013149.
Mo, R. F., Jin, J. Q., & Guo, X. Y. (2007). Materials Letters, 61, 3787–3790.
Chen, D., Gao, L., Yasumori, A., Kuroda, K., & Sugahara, Y. (2008). Single-crystalline tungsten oxide nanoplates. Small, 4, 1813–1822. http://waseda.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/singlecrystalline-tungsten-oxide-nanoplates(423bc3bc-6100-4f5d-9234-57a81c030533).html.
Soto, K., Garza, K. M., & Murr, L. E. (2007). Cytotoxic effects of aggregated nanomaterials. Acta Biomaterialia, 3, 351–358. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17275430.
Worle-Knirsch, J. M., Pulskamp, K., & Krug, H. F. (2006). Oops they did it again! Carbon nanotubes hoax scientists in viability assays. NanoLetters, 6, 1261–8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16771591.
Papageorgiou, I., Brown, C., Schins, R., Singh, S., Newson, R., Davis, S., Fisher, J., Ingham, E., & Case, C. P. (2007). The effect of nano- and micron-sized particles of cobalt-chromium alloy on human fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials, 2007(28), 2946–58. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.02.034. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=444551.
Weyrmann, J., Lochmann, D., & Zimmer, A. (2005). A practical note on the use of cytotoxicity assays. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2005(288), 369–76. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15620877.
Papageorgiou, I., Brown, C., Schins, R., Singh, S., Newson, R., Davis, S., Fisher, J., Ingham, E., & Case, C. P. (2007). The effect of nano- and micron-sized particles of cobalt-chromium alloy on human fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials, 28, 2946–58. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17379299.
Warburg, O. (1956). On the origin of cancer cells. Science, 123(3191), 309–14. doi:10.1126/science.123.3191.309. https://www.google.com.eg/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0CCUQFjABahUKEwjzpoD3o9THAhVGuBQKHdCDAN0&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencemag.org%2Fcontent%2F123%2F3191%2F309.long&ei=L8nkVbPTOsbwUtCHgugN&usg=AFQjCNEwPX441YjsMElR6JgeBuTBSrm4mw.
Wang, J., Chen, C., Liu, Y., Jiao, F., Li, W., Lao, F., Li, Y., Li, B., Ge, C., Zhou, G., Gao, Y., Zhao, Y., & Chai, Z. (2008). Potential neurological lesion after nasal instillation of TiO(2) nanoparticles in the anatase and rutile crystal phases. Toxicology Letters, 183(1–3), 72–80. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378427408012848.
Schanen, B. C., Karakoti, A. S., Seal, S., Warren, W. L., & William, T. (2011). Exposure to titanium dioxide nanomaterials provokes inflammation of an in vitro human immune construct. ACS Nano, 3(9), 2523–2532. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19769402.
MacNee, W., & Donaldson, K. (2003). Mechanism of lung injury caused by PM10 and ultrafine particles with special reference to COPD. The European Respiratory Journal Supplement, 40, 47s–51s. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12762574.
Elsabahy, M., & Wooley, K. (2013). Cytokines as biomarkers of nanoparticle immunotoxicity. Chemical Society Reviews, 42(12), 5552–5576. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23549679.
Barbasz, A., Oćwieja, M., & Barbasz, J. (2015). Cytotoxic activity of highly purified silver nanoparticles Sol against cells of human immune system. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176, 817–834. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Cytotoxic+Activity+of+Highly+Purified+Silver+Nanoparticles+Sol+Against+Cells+of+Human+Immune+System.
Rama, I., Bruene, B., Torras, J., Koehl, R., Cruzado, J. M., Bestard, O., Franquesa, M., Lloberas, N., Weigert, A., Herrero-Fresneda, I., Gulias, O., & Grinyó, J. M. (2008). Hypoxia stimulus: an adaptive immune response during dendritic cell maturation. Kidney International, 73(7), 816–25. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18216782.
Zhao, J., Bowman, L., Magaye, R., Leonard, S. S., Castranova, V., & Ding, M. (2013). Apoptosis induced by tungsten carbide-cobalt nanoparticles in JB6 cells involves ROS generation through both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways. International Journal of Oncology, 42(4), 1349–59. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23417053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yassin, A.M., Elnouby, M., El-Deeb, N.M. et al. Tungsten Oxide Nanoplates; the Novelty in Targeting Metalloproteinase-7 Gene in Both Cervix and Colon Cancer Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 180, 623–637 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2120-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2120-x