Abstract
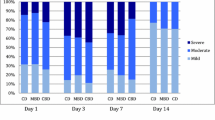
Tonsillectomy is one of the commonly performed otolaryngological operations. Despite a range of different techniques post-operative pain remains a major side-effect of this operation. Coblation assisted tonsillectomy is a latest technique of tonsillectomy. This technique is said to be associated with less intra-operative bleeding and less postoperative morbidity. We conducted a study in 100 patients to compare the pain scores between coblation assisted and bipolar diathermy tonsillectomy by FLACC score and Wong Baker scale score. The data so collected was statistically analysed using a t test and p values were calculated. The p value was highly significant (p < 0.001) for both scores in coblation assisted tonsillectomy 6 h postoperatively and on 1st postoperative day (p < 0.05). On 7th post-operative day however there was no significant difference in post-operative pain score using FLACC score in both groups but Wong baker scale scores were still significant. We concluded that post-operative pain was less with coblator assisted tonsillectomy as compared to bipolar diathermy tonsillectomy at least in early post-operative period.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowe D, van der Meulen J, Cromwell D, Lewsey J, Copley L, Browne J et al (2007) Key messages from the national prospective tonsillectomy audit. Laryngoscope 117(4):717–724
Pinder DK, Wilson H, Hilton MP (2011) Dissection versus diathermy for tonsillectomy. Cochrane Database Sys Rev (3):CD002211. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002211.pub2
Hesham A (2009) Bipolar diathermy versus cold dissection in paediatric tonsillectomy. Int J Paediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:793–795
Sergeev VN, Belov SV (2003) Coblation technology: a new method for high-frequency electrosurgery. Springer Biomed Eng 37(1):22–25
Nithya V, Dutta A, Sabari Girish K (2017) A comparative study of coblation assisted adenotonsillectomy and cold dissection adenotonsillectomy in children. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 3:122–127
Woloszko J, Gilbride C (2000) Coblation technology: plasma mediated ablation for otolaryngology applications. In: Proceedings of the SPIE, vol 3907, pp 306–316. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.386267
Balasubramanian (2014) Coblation tonsillectomy—our experience. Otolaryngology. ISSN:22500359.4(1.5). https://worldwidescience.org/topicpages/t/tonsillectomy. Accessed 3 May 2018
Temple RH, Timms MS (2001) Paediatric coblation tonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 61:195–198
Timms MS, Temple RH (2002) Coblation tonsillectomy: a double blind randomized controlled study. J Laryngolotol 116:450–452
The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne (2018) Clinical Guidelines (nursing). Pain Assess Meas. https://www.rch.org.au/rchcpg/hospital_clinical_guideline_index/Pain_Assessment_and_Measurement/. Accessed 3 May 2018
Mitic S, Tvinnereim M, Lie E, Saltyte BJ (2007) A pilot randomized controlled trial of coblation tonsillectomy versus dissection tonsillectomy with bipolar diathermy haemostasis. Clin Otolaryngol 32:261–267
Singh R, Anand TS, Garg P, Kulshreshtha P (2012) A prospective, randomized, double-blind study of coblation versus dissection tonsillectomy in adult patients. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64(3):290–294
Burton MJ, Doree C (2007) Coblation versus other surgical techniques for tonsillectomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3):CD004619. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004619.pub2
Noordzji JP, Affleck BD (2006) Coblation versus unipolar electrocautery tonsillectomy. Laryngoscope 116(8):1303–1309
Omrani M, Barati B, Omidifar N, Okhovvat A, Hashemi S (2012) Coblation versus traditional tonsillectomy: a double blind randomized controlled trial. J Res Med Sci 17(1):45–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhardwaj, B., Singh, J. Comparative Post-operative Pain Analysis Between Coblator Assisted and Bipolar Diathermy Tonsillectomy in Paediatric Patients. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71, 90–94 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1403-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1403-7