Abstract
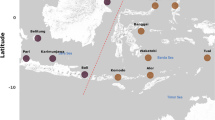
The spatial–temporal distribution of dinoflagellate cyst (i.e., dinocyst) communities is crucial for understanding the detailed mechanisms of recurrence and spread of harmful algae blooms in marine ecosystems. Here, we employed the newly developed high-throughput sequencing-based metabarcoding to characterize dinocyst communities collected from the South China Sea. Further, we clarified the spatial–temporal distribution patterns and analyzed the correlation between environmental factors and the observed patterns to investigate how they are influenced by environmental factors. Our results showed that the spatial distribution of dinocyst species richness and abundance varied greatly between sampling sites in different seasons. Both redundancy and Pearson analyses showed that the chemical oxygen femand, which could explained 35.0% of the total community variation, had positive correlations with heterotrophic dinocyst richness and negative correlations with autotrophic dinocysts richness. We did not find significant correlations between heavy metals and any features of dinocyst species richness. No environmental factor showed significant effects on dinocyst abundance based on forward selection after excluding colinearity; however, Pearson’s correlation analyses showed that the abundance of heterotrophic dinocysts presented a significant positive correlation with Mn (P < 0.05). Our results showed that the influence of environmental factors on spatial–temporal distribution of dinocyst species could be region- and/or environment-specific. Consequently, we suggest that detailed investigations should be performed to clarify the influence of varied environmental factors on dinocyst community characteristics in different regions and/or seasons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Alpermann TJ, Cembella AD, Collos Y, Masseret E, Montresor M (2012) The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 14:10–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2011.10.012
Anglès S, Garcés E, Hattenrath-Lehmann TK, Gobler CJ (2012) In situ life-cycle stages of Alexandrium fundyense during bloom development in Northport Harbor (New York, USA). Harmful Algae 16:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2011.12.008
Aydin H, Yürür EE, Uzar S, Küçüksezgin F (2015) Impact of industrial pollution on recent dinoflagellate cysts in Izmir Bay (eastern Aegean). Mar Pollut Bull 94:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.02.038
Bravo I, Figueroa R (2014) Towards an ecological understanding of dinoflagellate, cyst functions. Microorganisms 2:11–32. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms2010011
Dale B, Thorsen TA, Fjellsa A (1999) Dinoflagellate cysts as indicators of cultural eutrophication in the Oslofjord, Norway. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 48(3):371–382. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.1999.0427
Dray S, Legendre P, Peres-Neto PR (2006) Spatial modelling: a comprehensive framework for principal coordinate analysis of neighbor matrices (PCNM). Ecol Model 196(3-4):483–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.02.015
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2604
Gao Y, Fang H, Dong Y, Li H, Pu C, Zhan A (2017) An improved method for molecular identification of single dinoflagellate cysts. Peer J 5:e3224. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3224
Gowen RJ, Collos Y, Tett P, Scherer C, Bec B, Abadie E, Allen M, O'Brien T (2015) Response of diatom and dinoflagellate lifeforms to reduced phosphorus loading: a case study in the Thau lagoon, France. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 162:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.03.033
Head MJ (1996) Modern Dinofalgelate cysts and their biological affinities. In: Jansonius, McGregory DC (eds) Palynology: principles and applications. American Association of Stratigraphic Palynologists Foundation, Dallas, pp 1197–1248
Hirai J, Kuriyama M, Ichikawa T, Hidaka K, Tsuda A (2015) A metagenetic approach for revealing community structure of marine planktonic copepods. Mol Ecol Resour 15(1):68–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12294
Horner RA, Greengrove CL, Davies-Vollum KS, Gawel JE, Postel JR, Cox AM (2011) Spatial distribution of benthic cysts of Alexandrium catenella in surface sediments of Puget sound, Washington, USA. Harmful Algae 11:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2011.08.004
Kambura AK, Mwirichia RK, Kasili RW, Karanja EN, Makonde, Boga HI (2016) Bacteria and Archaea diversity within the hot springs of Lake Magadi and little Magadi in Kenya. BMC Microbiol 16:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-016-0748-x
Kang NS, Jeong HJ, Yoo YD, Yoon EY, Lee KH, Lee K, Kim G (2011) Mixotrophy in the newly described phototrophic dinoflagellate Woloszynskia cincta from western Korean waters: feeding mechanism, prey species and effect of prey concentration. J Eukaryot Microbiol 58(2):152–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2011.00531.x
Ki JS (2012) Hypervariable regions (V1-V9) of the dinoflagellate 18S rRNA using a large dataset for marker considerations. J Appl Phycol 24:1035–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9730-z
Kremp A, Elbrachler M, Schweikerl M, Wolny JL, Gottschling M (2005) Woloszynskia halophile (Biecheler) comb. Nov.: a bloom-forming cold-water dinoflagellate co-occurring with Scrippsiella hangoei (Dinophyceae) in the Baltic Sea. J Phycol 41:629–642. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00070.x
Lepš J, Šmilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lin S, Wang L, Zheng L, Dong Y, Liu S, Ding S, Ye N, Cao W, Zhuang Z (2014) Current status and future prospect of DNA barcoding in marine biology. Acta Oceanol Sin 36:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.12.001
Liu D, Shi Y, Di B, Sun Q, Wang Y, Dong Z, Shao H (2012) The impact of different pollution sources on modern dinoflagellate cysts in Sishili Bay, Yellow Sea, China. Mar Micropaleontol 84:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marmicro.2011.11.001
Massana R, Gobet A, Audic S, Bass D, Bittner L, Boutte C et al (2015) Marine protist diversity in European coastal waters and sediments as revealed by HTS. Environ Microbiol 17:4035–4049. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12955
Matsuoka K, Fukuyo Y (2000) Technical guide for modern dinoflagellate cyst study. WESTPAC-HAB, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Tokyo
Matsuoka K (2001) Further evidence for a marine dinoflagellate cyst as an indicator of eutrophication in Yokohama port, Tokyo Bay, Japan. Comments on a discussion by B. Dale. Sci Total Environ 264(3):221–233
Melo F, Nascimento C, Souza DO, Albuquerque RF (2016) Identification of oral bacteria on titanium implant surfaces by 16S rDNA sequencing. Clin Oral Implants Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12865
Okamoto OK, Shao L, Hastings JW, Colepicolo P (1999) Acute and chronic effects of toxic metals on viability, encystment and bioluminescence in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polyedra. Comp Biochem Physiol C 123:75–83
Pandeirada MS, Craveiro SC, Calado AJ (2013) Freshwater dinoflagellates in Portugal (W Iberia): a critical checklist and new observations. Nova Hedwigia 97(3-4):321–348. https://doi.org/10.1127/0029-5035/2013/0119
Parameswaran P, Jalili R, Tao L, Shokralla S, Gharizadeh B, Ronaghi M, Fire AZ (2007) A pyrosequencing-tailored nucleotide barcode design unveils opportunities for large-scale sample multiplexing. Nucleic Acids Res 35:e130. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm760
Penna A, Battocchi C, Garcés E, Anglès S, Cucchiari E, Totti C, Kremp A, Satta C, Giacobbe MG, Bravo I (2010) Detection of microalgal resting cysts in European coastal sediments using a PCR-based assay. Deep-Sea Res Part II 57:288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.09.010
Persson A, Godhe A, Karlson B (2000) Dinoflagellate cysts in recent sediments from the west coast of Sweden. Bot Mar 43:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1515/BOT.2000.006
Pospelova V, Chmura GL, Boothman WS, Latimer JS (2002) Dinoflagellate cyst records and human disturbance in two neighboring estuaries, New Bedford Harbor and Apponagansett Bay, Massachusetts (USA). Sci Total Environ 298:81–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00195-X
Pospelova V, Chmur GL, Boothman WS, Latimer JS (2005) Spatial distribution of modern dinoflagellate cysts in polluted estuarine sediments from Buzzards Bay (Massachussetts, USA) embayments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 292:23–40. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps292023
Rämä T, Davey ML, Nordén J, Halvorsen R, Blaalid R, Mathiassen GH, Alsos IG, Kauserud H (2016) Fungi sailing the Arctic Ocean: speciose communities in north atlantic driftwood as revealed by high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Microb Ecol 72:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0778-9
Rodríguez F, Varela M, Fernández E, Zapata M (2003) Phytoplankton and pigment distributions in an anticyclonic slope water oceanic eddy (SWODDY) in the southern Bay of Biscay. Mar Biol 143:995–1011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1129-1
Satta CT, Anglès S, Lugliè A, Guillén J, Sechi N, Camp J, Garcés E (2013) Studies on dinoflagellate cyst assemblages in two estuarine Mediterranean bays: a useful tool for the discovery and mapping of harmful algal species. Harmful Algae 24:65–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2013.01.007
Satta CT, Anglès S, Garcés E, Sechi N, Pulina S, Padedda BM, Stacca D, Lugliè A (2014) Dinoflagellate cyst assemblages in surface sediments from three shallow Mediterranean lagoons (Sardinia, north western Mediterranean Sea). Estuar Coasts 37:646–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-013-9705-1
Sildever S, Andersen TJ, Ribeiro S, Ellegaard M (2015) Influence of surface salinity gradient on dinoflagellate cyst community structure, abundance and morphology in the Baltic Sea, Kattegat and Skagerrak. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 155:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.01.003
Sun C, Zhao Y, Li H, Dong Y, MacIsaac HJ, Zhan A (2015) Unreliable quantitation of species abundance based on high-throughput sequencing data of zooplankton communities. Aquat Biol 24:9–15. https://doi.org/10.3354/ab00629
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tang CQ, Leasi F, Obertegger U, Kieneke A, Barraclough TG, Fontaneto D (2012) The widely used small subunit 18S rDNA molecule greatly underestimates true diversity in biodiversity surveys of the meiofauna. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:16208–16212. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209160109
Tsirtsis G, Karydis M (1998) Evaluation of phytoplankton community indices for detecting eutrophic trends in the marine environment. Environ Monit Assess 50(3):255–269. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005883015373
Větrovský T, Baldrian P (2013) Analysis of soil fungal communities by amplicon pyrosequencing: current approaches to data analysis and the introduction of the pipeline SEED. Biol Fertil Soils 49:1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22096
Wang Z, Matsuoka K, Qi Y, Chen J, Lu S (2004) Dinoflagellate cyst records in recent sediments from Daya bay, South China Sea. Phycol Res 52(4):396–407. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-183.2004.00357.x
Wang Z, Fu Y, Kang W, Liang J, Gu Y, Jiang X (2013) Germination of phytoplankton resting cells from surface sediments in two areas of the southern Chinese coastal waters. Mar Ecol 34:218–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12009
Xiong W, Li H, Zhan A (2016) Early detection of invasive species in marine ecosystems using high-throughput sequencing: technical challenges and possible solutions. Mar Biol 163(6):139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2911-1
Xiong W, Ni P, Chen Y, Gao Y, Shan B, Zhan A (2017) Zooplankton community structure along a pollution gradient at fine geographical scales in river ecosystems: the importance of species sorting over dispersal. Mol Ecol 26:4351–4360. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.14199
Zhan A, Hulák M, Sylvester F, Huang X, Adebayo AA, Abbott CL, Adamowicz SJ, Heath DD, Cristescu ME, MacIsaac HJ (2013) High sensitivity of 454 pyrosequencing for detection of rare species in aquatic communities. Methods Ecol Evol 4:558–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12037
Zhan A, Bailey SA, Heath DD, Macisaac HJ (2014) Performance comparison of genetic markers for high-throughput sequencing-based biodiversity assessment in complex communities. Mol Ecol Resour 14:1049–1059. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12044
Zhan A, MacIsaac HJ (2015) Rare biosphere exploration using high-throughput sequencing: research progress and perspectives. Conserv Genet 16(3):513–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-014-0678-9
Žifčáková L, Větrovský T, Howe A, Baldrian P (2016) Microbial activity in forest soil reflects the changes in ecosystem properties between summer and winter. Environ Microbiol 18:288–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13026
Zonneveld KAF, Marret F, Versteegh GJ, Bogus K, Bonnet S, Bouimetarhan I et al (2013) Atlas of modern dinoflagellate cyst distribution based on 2405 data points. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 191:1–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.revpalbo.2012.08.003
Zonneveld KAF, Pospelova V (2015) A determination key for modern dinoflagellate cysts. Palynology 39(3):387–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/01916122.2014.990115
Acknowledgement
This work was partially supported by the 100-Talent Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences to A.Z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.Z., H.L. and Y.D. conceived the study. Y.G., Y.D., H.L and A.Z. designed the experiment. Y.G. and H.L. conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. Y.G., Y.D., H.L and A.Z. wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Sampling and field studies
All necessary permits for sampling and observational field studies have been obtained by the authors from the competent authorities and are mentioned in the acknowledgements, if applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by B. Beszteri
Yangchun Gao and Yanhong Dong contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 16825 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Dong, Y., Li, H. et al. Influence of environmental factors on spatial–temporal distribution patterns of dinoflagellate cyst communities in the South China Sea. Mar Biodiv 49, 769–781 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-018-0850-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-018-0850-4