Abstract
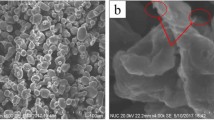
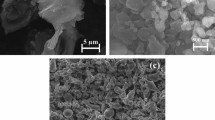
To study the influence of rolling on the interfaces and mechanical performance of graphene-reinforced Al-matrix composites, a rolling method was used to process them. Using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, and tensile testing, this study analyzed the micromorphology, interfaces, and mechanical performance of the composites before and after rolling. The experimental results demonstrates that the composites after hot rolling has uniform structures with strong interfacial bonding. With an increase in rolling temperature, the tensile strength and elastic modulus of the composites gradually increase. However, when the rolling temperature is higher than 500°C, granular and rod-like Al4C3 phases are observed at the interfaces and the mechanical performance of the composites is degraded. When the rolling temperature is 480°C, the composites show the optimal comprehensive mechanical performance, with a tensile strength and elastic modulus of 403.3 MPa and 77.6 GPa, respectively, which represent increases of 31.6% and 36.9%, respectively, compared with the corresponding values prior to rolling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Zhang, G.D. Zhang, and Z.Q. Li, The current state and trend of metal matrix composites, Mater. China, 29(2010), No. 4, p. 1.
J. Joel and M.A. Xavior, Aluminium alloy composites and its machinability studies; A review, Mater. Today Proc., 5(2018), No. 5, p. 13556.
M.K. Surappa, Aluminium matrix composites: Challenges and opportunities, Sadhana, 28(2003), No. 1–2, p. 319.
I.A. Ibrahim, F.A. Mohamed, and E.J. Lavernia, Particulate reinforced metal matrix composites—a review, J. Mater. Sci., 26(1991), No. 5, p. 1137.
R.R. Nair, P. Blake, A.N. Grigorenko, K.S. Novoselov, T.J. Booth, T. Stauber, N.M.R. Peres, and A.K. Geim, Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene, Science, 320(2008), No. 5881, p. 1308.
A.K. Geim, Graphene: Status and prospects, Science, 324(2009), No. 5934, p. 1530.
R.F. Service, Carbon sheets an atom thick give rise to graphene dreams, Science, 324(2009), No. 5929, p. 875.
C. Lee, X.D. Wei, J.W. Kysar, and J. Hone, Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene, Science, 321(2008), No. 5887, p. 385.
R.T. Weitz and A. Yacoby, Nanomaterials: graphene rests easy, Nat. Nanotechnol., 5(2010), No. 10, p. 699.
A.A. Balandin, S. Ghosh, W.Z. Bao, I. Calizo, D. Teweldebrhan, F. Miao, and C.N. Lau, Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene, Nano. Lett., 8(2008), No. 3, p. 902.
M.F.L.D. Volder, S.H. Tawfick, R.H. Baughman, and A.J. Hart, Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications, Science, 339(2013), No. 6119, p. 535.
M.A. Rafiee, J. Rafiee, Z. Wang, H.H. Song, Z.Z. Yu, and N. Koratkar, Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocomposites at low graphene content, ACS Nano, 3(2009), No. 12, p. 3884.
A. Bisht, M. Srivastava, R.M. Kumar, I. Lahiri, and D. Lahiri, Strengthening mechanism in graphene nanoplatelets reinforced aluminum composite fabricated through spark plasma sintering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 695(2017), p. 20.
X. Zeng, J. Teng, J.G. Yu, A.S. Tan, D.F. Fu, and H. Zhang, Fabrication of homogeneously dispersed graphene/Al composites by solution mixing and powder metallurgy, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater, 25(2018), No. 1, p. 102.
S.E. Shin, H.J. Choi, J.H. Shin, and D.H. Bae, Strengthening behavior of few-layered graphene/aluminum composites, Carbon, 82(2015), p. 143.
W.M. Tian, S.M. Li, B. Wang, X. Chen, J.H. Liu, and M. Yu, Graphene-reinforced aluminum matrix composites prepared by spark plasma sintering, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 23(2016), No. 6, p. 723.
G.H. Wu, L.T. Jiang, G.Q. Chen, and Q. Zhang, Research progress on the control of interfacial reactions in metal matrix composites, Mater. China, 31(2012), No. 7, p. 51.
T.P.D. Rajan, R.M. Pillai, and B.C. Pai, Reinforcement coatings and interfaces in aluminium metal matrix composites, J. Mater. Sci., 33(1998), No. 14, p. 3491.
J.L. Lin, Y.C. Xiong, X.D. Wang, S.J. Yan, C. Yang, W.W. He, J.Z. Chen, S.Q. Wang, X.Y. Zhang, and S.L. Dai, Microstructure and tensile properties of bulk nanostructured aluminum/graphene composites prepared via cryomilling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 626(2015), p. 400.
R. Pérez-Bustamante, F. Pérez-Bustamante, I. Estrada-Guel, L. Licea-Jiménez, M. Miki-Yoshida, and R. Martínez-Sánchez, Effect of milling time and CNT concentration on hardness of CNT/Al2024 composites produced by mechanical alloying, Mater Charact., 75(1970), p. 13.
G. Li and B.W. Xiong, Effects of graphene content on microstructures and tensile property of graphene-nanosheets / aluminum composites, J. Alloys. Compd., 697(2017), p. 31.
S.E. Shin, Y.J. Ko, and D.H. Bae, Mechanical and thermal properties of nanocarbon-reinforced aluminum matrix composites at elevated temperatures, Composites. Part. B, 106(2016), p. 66.
J.Y. Wang, Z.Q. Li, G.L. Fan, H.H. Pan, Z.X. Chen, and D. Zhang, Reinforcement with graphene nanosheets in aluminum matrix composites, Scr. Mater., 66(2012), No. 8. p. 594.
A. Radha and K.R. Vijayakumar, An investigation of mechanical and wear properties of AA6061 reinforced with silicon carbide and graphene nano particles-particulate composites, Mater. Today: Proc., 3(2016), No. 6, p. 2247.
Acknowledgement
The work was financially supported by the National Key Development Program of China for the “13th Five-Year Plan” (No. 2016YFB0700300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Cy., Hu, Sp. & Chen, K. Influence of rolling temperature on the interfaces and mechanical performance of graphene-reinforced aluminum-matrix composites. Int J Miner Metall Mater 26, 752–759 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1780-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1780-2