Abstract
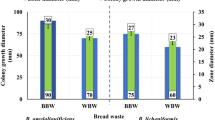
In the present study a fungi was newly isolated from municipal dumping area of Midnapore town, West Bengal, India for the production of α-amylase. The isolate was identified as Aspergillus niger RBP7 (KX100578.1) through phenotypic and 18S rDNA sequencing observation. It produced clear zone (6.2 mm) on Czapekdox agar medium fortified with starch (1%, w/v). Optimization of enzyme production was studied under solid state fermentation (SSF) using potato peel as a substrate by one-variable-at-a-time (OVAT) and followed with response surface methodology (RSM), which enhanced enzyme titer up to 1112.25 U/gds with an initial medium pH-3.0. The texture of the potato peel before and after the fermentation was studied by FTIR. After fermentation the cell free supernatant was significantly effective for hydrolysis of raw starchy food stuff (taro, yam, malanga and sweet potato) and also able to produce mono-meric and dimeric sugars-like glucose and maltose. These characteristics of the enzyme may be suitable for use to treat digestive dysfunction.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raghu, H.S., Rajeshwara, N.A.: Immobilization of α-amylase (1,4-α-d glucanglucano hydralase) by calcium alginate encapsulation. Int. Food Res. J. 22, 869–871 (2015)
Jana, M., Pati, B.: Thermostable, salt-tolerant a-amylase from Bacillus sp. MD 124. J. Basic Microbiol. 37, 323–326 (1997)
Abou-Elela, G.M., Nermeen, A.E., Wefky, S.H.: Statistical optimization of cold adapted α-amylase production by free and immobilized cells of Nocardiopsis aegyptia. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 5(3), 286–292 (2009)
Dey, G., Mitra, A., Banerjee, R., Maiti, B.R.: Enhanced production of amylase by optimization of nutritional constituents using response surface methodology. Biochem. Eng. J. 7, 227–231 (2001)
Aiyer, P.V.D.: Effect of C:N ratio on alpha amylase production by Bacillus licheniformis SPT 27. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 3, 519–522 (2004)
Alva, S., Anupama, J., Savia, J., Chiu, Y.Y.: Characterization of fungal amylase enzyme isolated from Aspergillus sp. JGI 12 in solid state culture. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 6, 576–581 (2005)
Baig, M.M.V., Baig, M.L.B., Baig, M.A.I., Yasmeen, M.: Saccharification of banana agro-waste by cellulytic enzymes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 3, 447–450 (2004)
Baks, T., bruins, M.E., Matser, A.M., Jansen, A.E.M., Boom, R.M.: Effect of gelatinization and hydrolysis conditions on the selectively of starch hydrolysis with alpha amylase from Bacillus licheniformis. J. Agri. Food Chem. 56, 488–495 (2008)
Pandey, A., Nigam, P., Soccol, V.T., Singh, D., Mohan, R.: Advances in microbial amylases. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 31, 135–152 (2000)
Bernfeld, P.: Amylases, α and β. In: Methods in enzymology. New York, Academic Press (1955)
Reddy, N., Yang, Y.: Properties of high-quality long natural cellulose fibers from rice straw. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 8077–8081 (2006)
Mishra, S., Noronha, S.B., Suraishkumar, G.K.: Increase in enzyme productivity by induced oxidative stress in Bacillus subtilis cultures and analysis of its mechanism using microarray data. Process Biochem. 40, 1863–1870 (2005)
Okolo, B.N., Ire, F.S., Ezeogu, L.I., Anyanwu, C.U., Odibo, F.J.C.: Purification and some properties of a noval starch digesting amylase from Aspergillus carbonarius. J. Sci. Food Agric. 81(3), 329–336 (2000)
Forgarty, W.M., Kelly, C.T.: Developments in microbial extracellular enzymes. In: Wiseman, E.A. (ed.) Topics in enzyme and fermentation biotechnology, vol. 3, pp. 45–108. Applied Science Publishers, London (1979)
Sivaramakrishnan, S., Gangadharan, D., Nampoothiri, K.M., Carlos Ricardo Soccol, C.R., Pandey, A.: α-Amylases from microbial sources: an overview on recent developments. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 44(2), 173–184 (2006)
Pederson, H., Nielson, J.: The influence of nitrogen sources on the α-amylase productivity of Aspergillus oryzae in continuous cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 53, 278–281 (2000)
Taniguchi, H., Odashima, F., Igarashi, M., Maruyama, Y., Nkamura, M.: Characterization of a potato starch digesting bacterium and its production of amylase. Agric. Biol. Chem. 46, 2107–2115 (1982)
Mitchell, D.A., Lonsane, B.K.: General principles of solid state fermentation, monogramed by Doelle HW, Rolz C. Publication of Oxford, London (1990)
Laddish, M.R., Lin, K.W., Voloch, M., Tsao, G.T.: Process consideration in the enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass. Enzyme Microbial. Technol. 5, 8–16 (1983)
Gautam, B., Karki, B.T., Panta, O.P.: Optimization of cultural conditions for solid state fermentation of amylase production by Aspergillus species. NepJOL. 14(1), 67–74 (2013)
Suganthi, R., Benazir, J.F., Santhi, R., Ramesh Kumar, V., Hari, A., Meenakshi, N., Nidhiya, K.A., Kavitha, G., Lakshmi, R.: Amylase production by Aspergillus niger under solid state fermentation using agroindustrial waste. IJEST. 3(2), 1756–1763 (2011)
Raul, D., Biswas, T., Mukhopadhyay, S., Das, K.S., Gupta, S.: Production and partial purification of alpha amylase from Bacillus subtilis (MTCC 121) using solid state fermentation. Biochem. Res. Int. 2014, 568141 (2014)
Liang, S., McDonald, A.G.: Chemical and thermal characterization of potato peel waste and its fermentation residue as potential resources for biofuel and bioproducts production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 8421–8429 (2014)
Bergmann, F.W., Abe, J., Hizukuri, S.: Selection of micro-organisms which produce raw starch degrading amylases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27, 443–446 (1988)
Cheesbrough, M.: District laboratory practice in tropical countries, 2nd edn., SheckWah Tong Printing Press Ltd., Hong Kong, pp. 362–363 (2005)
Swain, M.R., Ray, R.C.: Alpha-amylase production by Bacillus subtilis CM3 in solid state fermentation using cassava fibrous residue. J. Basic Microbiol. 47, 417–425 (2007)
Poddar, A., Gachhui, R., Jana, S.C.: Optimization of physico-chemical condition for improved production of hyper thermostable β amylase from Bacillus subtilis DJ5. J. Biochem. Tech. 3, 370–374 (2012)
Nguyen, Q.D., Rezessy-Szabo, J.M., Hoschke, A.: Optimization of composition of media for the production of amylolytic enzymes by Thermomyces lanuginosus ATCC 34626. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 38, 229–234 (2000)
Bedan, D.S., Aziz, G.M., AlSa’ady, A.J.R.: Optimum conditions for α-amylase production by Aspergillus niger mutant isolate using solid state fermentation. Curr. Res. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2, 450–456 (2014)
Deng, S., Yu, G., Ting, Y.P.: Production of a bioflocculant by Aspergillus parasiticus and its application in dye removal. Colloids Surf. B. 44, 179–186 (2005)
Kalaiarasi, K., Ramasamy, P.: Optimization of process parameters for α-amylase production under solid-state fermentation by Bacillus cereus MTCC 10202. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 7(45), 5166–5177 (2013)
Mishra, A., Kavita, K., Jha, B.: Characterization of extracellular polymeric substance produced by micro-algae Dunaliellasalina. Carb Pol. 82, 852–857 (2011)
Dash, K.B., Rahman, M.M., Sarker, K.P.: Molecular identification of a newly isolated Bacillus subtilis BI19 and optimization of production conditions for enhanced production of extracellular amylase. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 859805 (2015)
Sindhu, R., Suprabha, G.N., Shashidhar, S.: Optimization of process parameters for the production of α-amylase from Penicillium janthinellum (NCIM 4960) under solid state fermentation. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 3(9), 498–503 (2009)
Hassan, H., Khairiah, A.K.: Optimization of alpha amylase production from rice straw using solid-state fermentation of Bacillus subtilis. IJEST 4, 1–16 (2015)
Eman, A.K., Walaa, A.A.W., Shireen, A.A. S., Mohamed, E.H., Amany, L.K., Mona, A.E.: Production, simmobilization and thermodynamic studies of free and immobilized Aspergillus awamori amylase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 102, 694–703 (2017)
Pereiraa, C.R., Resendea, J.T.V., Guerraa, E.P., Limab, V.A., Martinsa, M.D., Knob, A.: Enzymatic conversion of sweet potato granular starch into fermentable sugars: feasibility of sweet potato peel as alternative substrate for α-amylase production. ISBAB 11, 231–238 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Central Research Facility, Indian Institute Of Technology, Kharagpur, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, R., Paul, T., Soren, J.P. et al. Acidophilic α-Amylase Production from Aspergillus niger RBP7 Using Potato Peel as Substrate: A Waste to Value Added Approach. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 851–863 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0114-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0114-8