Abstract
Purpose of Review
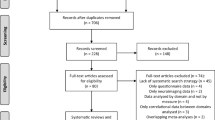
To conduct a systematic review of recent case-control studies investigating the similarities and differences between gambling disorder (GD), substance use disorders (SUDs), and behavioral addictions (BAs).
Recent Findings
A total of 36 studies were identified for synthesis, with 56% comparing GD to SUDs, 36.11% comparing GD to other BAs, and 8.33% comparing to both. The results indicated that GD and SUDs/BAs do not present with overall differences in neurocognitive, clinical, and impulsivity dimensions. Rather, GD is associated with more nuanced differences in these dimensions. In contrast, GD was likely to present with significant differences in personality although with conflicting results in the directionality and dimensions of the personality trait compared to SUDs/BAs.
Summary
GD warrants classification as a disorder due to addictive behaviors. However, nuanced differences exist between GD and SUDs/BAs, which should be taken into account in the conceptualization of GD as an addiction.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
DSM 5. DSM 5. Am J Psychiatr 2013. 991
Saunders JB. Substance use and addictive disorders in DSM-5 and ICD 10 and the draft ICD 11. Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 2017;30:227–37.
Grant JE, Potenza MN, Weinstein A, Gorelick DA. Introduction to behavioral addictions. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2010;36(5):233–41.
Goudriaan AE, Oosterlaan J, De Beurs E, Van Den Brink W. Pathological gambling: a comprehensive review of biobehavioral findings. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:123–41.
Petry NM. Should the scope of addictive behaviors be broadened to include pathological gambling? Addiction. 2006;101:152–60.
Albein-Urios N, Martinez-González JM, Lozano Ó, Clark L, Verdejo-García A. Comparison of impulsivity and working memory in cocaine addiction and pathological gambling: implications for cocaine-induced neurotoxicity. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012;126:1–2):1–6.
Tavares H, Zilberman ML, Hodgins DC, el-Guebaly N. Comparison of craving between pathological gamblers and alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29(8):1427–31.
Castellani B, Rugle L. A comparison of pathological gamblers to alcoholics and cocaine misusers on impulsivity, sensation seeking, and craving. Subst Use Misuse. 1995;30(3):275–89.
Lee HW, Choi J-S, Shin Y-C, Lee J-Y, Jung HY, Kwon JS. Impulsivity in internet addiction: a comparison with pathological gambling. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2012;15(7):373–7.
Ciarrocchi JW, Kirschner NM, Fallik F. Personality dimensions of male pathological gamblers, alcoholics, and dually addicted gamblers. J Gambl Stud. 1991;7(2):133–41.
Orford J, Morison V, Somers M. Drinking and gambling: a comparison with implications for theories of addiction. Drug and Alcohol Review. 1996;15:47–56.
Ciarrocchi J, Hohmann AA. The family environment of married male pathological gamblers, alcoholics, and dually addicted gamblers. J Gambl Behav. 1989;5(4):283–91.
Goudriaan AE, Oosterlaan J, De Beurs E, Van Den Brink W. Neurocognitive functions in pathological gambling: a comparison with alcohol dependence, Tourette syndrome and normal controls. Addiction. 2006;101(4):534–47.
Gearhardt AN, White MA, Potenza MN. Binge eating disorder and food addiction. Curr Drug Abus Rev. 2011;4(3):201–7.
Smith DG, Robbins TW. The neurobiological underpinnings of obesity and binge eating: a rationale for adopting the food addiction model. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:804–10.
Contreras-Rodríguez O, Albein-Urios N, Vilar-López R, Perales JC, Martínez-Gonzalez JM, Fernández-Serrano MJ, et al. Increased corticolimbic connectivity in cocaine dependence versus pathological gambling is associated with drug severity and emotion-related impulsivity. Addict Biol. 2016;21(3):709–18.
Contreras-Rodríguez O, Albein-Urios N, Perales JC, Martínez-Gonzalez JM, Vilar-López R, Fernández-Serrano MJ, et al. Cocaine-specific neuroplasticity in the ventral striatum network is linked to delay discounting and drug relapse. Addiction. 2015;110(12):1953–62.
Romanczuk-Seiferth N, Koehler S, Dreesen C, Wüstenberg T, Heinz A. Pathological gambling and alcohol dependence: neural disturbances in reward and loss avoidance processing. Addict Biol. 2015;20(3):557–69.
Worhunsky PD, Malison RT, Rogers RD, Potenza MN. Altered neural correlates of reward and loss processing during simulated slot-machine fMRI in pathological gambling and cocaine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;145:77–86.
Worhunsky PD, Potenza MN, Rogers RD. Alterations in functional brain networks associated with loss-chasing in gambling disorder and cocaine-use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;178:363–71.
• Bae S, Han DH, Jung J, Nam KC, Renshaw PF. Comparison of brain connectivity between Internet gambling disorder and Internet gaming disorder: a preliminary study. J Behav Addict. 2017;6(4):1–11 One of the only studies to compare functional connectivity between gambling disorder and another behavioral addiction.
Bae S, Hong JS, Kim SM, Han DH. Bupropion shows different effects on brain functional connectivity in patients with internet-based gambling disorder and internet gaming disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9(APR).
Sen YW, Li YH, Xiao L, Zhu N, Bechara A, Sui N. Working memory and affective decision-making in addiction: a neurocognitive comparison between heroin addicts, pathological gamblers and healthy controls. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;134(1):194–200.
Bottesi G, Ghisi M, Ouimet AJ, Tira MD, Sanavio E. Compulsivity and impulsivity in pathological gambling: does a dimensional-transdiagnostic approach add clinical utility to DSM-5 classification? J Gambl Stud. 2015;31(3):825–47.
Kräplin A, Bühringer G, Oosterlaan J, Van den Brink W, Goschke T, Goudriaan AE. Dimensions and disorder specificity of impulsivity in pathological gambling. Addict Behav. 2014;39(11):1646–51.
Mallorquí-Bagué N, Fagundo AB, Jimenez-Murcia S, De La Torre R, Baños RM, Botella C, et al. Decision making impairment: a shared vulnerability in obesity, gambling disorder and substance use disorders? Weinstein AM, editor PLoS One 2016;11(9):e0163901.
Zhou Z, Zhou H, Zhu H. Working memory, executive function and impulsivity in internet-addictive disorders: a comparison with pathological gambling. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2016;28(2):92–100.
Vanes LD, van Holst RJ, Jansen JM, van den Brink W, Oosterlaan J, Goudriaan AE. Contingency learning in alcohol dependence and pathological gambling: learning and unlearning reward contingencies. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014;38(6):1602–10.
Torres A, Catena A, Cándido A, Maldonado A, Megías A, Perales JC. Cocaine dependent individuals and gamblers present different associative learning anomalies in feedback-driven decision making: a behavioral and ERP study. Front Psychol. 2013;4(MAR):122.
• Majuri J, Joutsa J, Johansson J, Voon V, Alakurtti K, Parkkola R, et al. Dopamine and opioid neurotransmission in behavioral addictions: a comparative PET study in pathological gambling and binge eating. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;42(5):1169–77 One of the only studies to compare neurotransmitter functioning in gambling disorder and behavioral addictions.
Majuri J, Joutsa J, Johansson J, Voon V, Parkkola R, Alho H, et al. Serotonin transporter density in binge eating disorder and pathological gambling: a PET study with [11C]MADAM. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;27(12):1281–8.
Yip S, Morie K, Xu J, …, RC-B psychiatry, 2017 U. Shared microstructural features of behavioral and substance addictions revealed in areas of crossing fibers. Biol Psychiatry 2017;2(2):188–95.
Yip SW, Worhunsky PD, Xu J, Morie KP, Constable RT, Malison RT, et al. Gray-matter relationships to diagnostic and transdiagnostic features of drug and behavioral addictions. Addict Biol. 2018;23(1):394–402.
Kober H, Lacadie CM, Wexler BE, Malison RT, Sinha R, Potenza MN. Brain activity during cocaine craving and gambling urges: an fMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016;41(2):628–37.
Ren Y, Fang J, Lv J, Hu X, Guo CC, Guo L, et al. Assessing the effects of cocaine dependence and pathological gambling using group-wise spare representation of natural stimulus fMRI data. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017;11(4):1179–91.
•• Zilberman N, Yadid G, Efrati Y, Neumark Y, Rassovsky Y. Personality profiles of substance and behavioral addictions. Addict Behav. 2018;82:174–81 This study was one of the more comprehensive case-control studies. It compared gambling disorder to both behavioral addictions and substance use disordere on personality and impulsivity.
Müller KW, Dreier M, Beutel ME, Wölfling K. Is sensation seeking a correlate of excessive behaviors and behavioral addictions? A detailed examination of patients with gambling disorder and internet addiction. Psychiatry Res. 2016;242:319–25.
Choi S-W, Kim H, Kim G-Y, Jeon Y, Park S, Lee J-Y, et al. Similarities and differences among internet gaming disorder, gambling disorder and alcohol use disorder: a focus on impulsivity and compulsivity. J Behav Addict. 2014;3(4):246–53.
Albein-Urios N, Martinez-González JM, Lozano Ó, Verdejo-Garcia A. Monetary delay discounting in gambling and cocaine dependence with personality comorbidities. Addict Behav. 2014;39(11):1658–62.
del Pino-Gutiérrez A, Jiménez-Murcia S, Fernández-Aranda F, Agüera Z, Granero R, Hakansson A, et al. The relevance of personality traits in impulsivity-related disorders: from substance use disorders and gambling disorder to bulimia nervosa. J Behav Addict. 2017;6(3):396–405.
Mallorquí-Bagué N, Fernández-Aranda F, Lozano-Madrid M, Granero R, Mestre-Bach G, Baño M, et al. Internet gaming disorder and online gambling disorder: clinical and personality correlates. J Behav Addict. 2017;6(4):669–77.
Farré JM, Fernández-Aranda F, Granero R, Aragay N, Mallorquí-Bague N, Ferrer V, et al. Sex addiction and gambling disorder: similarities and differences. Compr Psychiatry. 2015;56:59–68.
Granero R, Fernández-Aranda F, Mestre-Bach G, Steward T, Baño M, del Pino-Gutiérrez A, et al. Compulsive buying behavior: clinical comparison with other behavioral addictions. Front Psychol. 2016;7(JUN):914.
Jiménez-Murcia S, Granero R, Moragas L, Steiger H, Israel M, Aymamí N, et al. Differences and similarities between bulimia nervosa, compulsive buying and gambling disorder. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2015;23(2):126–32.
Granero R, Fernández-Aranda F, Steward T, Mestre-Bach G, Baño M, del Pino-Gutiérrez A, et al. Compulsive buying behavior: characteristics of comorbidity with gambling disorder. Front Psychol. 2016;7(APR):625.
Tonioni F, Mazza M, Autullo G, Cappelluti R, Catalano V, Marano G, et al. Is Internet addiction a psychopathological condition distinct from pathological gambling? Addict Behav. 2014;39(6):1052–6.
Grbeša L, Martinac M, Romić M, Palameta N, Soldo V. Personality of alcoholics and gamblers in the Union of Clubs of Treated Alcoholics and Gamblers. Alcohol Psychiatry Res. 2016;52(2):125–32.
Müller KW, Beutel ME, Egloff B, Wölfling K. Investigating risk factors for internet gaming disorder: a comparison of patients with addictive gaming, pathological gamblers and healthy controls regarding the big five personality traits. Eur Addict Res. 2014;20(3):129–36.
Gavriel-Fried B, Rabayov T. Similarities and differences between individuals seeking treatment for gambling problems vs. alcohol and substance use problems in relation to the progressive model of self-stigma. Front Psychol. 2017;8(JUN):957.
Schwaninger PV, Mueller SE, Dittmann R, Poespodihardjo R, Vogel M, Wiesbeck GA, et al. Patients with non-substance-related disorders report a similar profile of childhood trauma experiences compared to heroin-dependent patients. Am J Addict. 2017;26(3):215–20.
Manning V, Koh PK, Yang Y, Ng A, Guo S, Kandasami G, et al. Suicidal ideation and lifetime attempts in substance and gambling disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2015;225(3):706–9.
Derogatis L, Unger R. Symptom checklist-90 revised. Corsini Encycl Psychol 2010;1–2.
Hindmarch I, Kerr JS, Sherwood N. The effects of alcohol and other drugs on psychomotor performance and cognitive function. Alcohol Alcohol. 1991;26(1):71–9.
Shaffer HJ, LaPlante DA, LaBrie RA, Kidman RC, Donato AN, Stanton MV. Toward a syndrome model of addiction: multiple expressions, common etiology. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2004;12(6):367–74.
Billieux J, Schimmenti A, Khazaal Y, Maurage P, Alexandre H. Are we overpathologizing everyday life? A tenable blueprint for behavioral addiction research. J Behav Addict. 2015;4(3):119–23.
Kim HS, Hodgins DC. Component model of addiction treatment: a pragmatic transdiagnostic treatment model of behavioral and substance addictions. Front Psychiatry 2018;9(403).
Hodgins DC, Stea JN, Grant JE. Gambling disorders. Lancet. 2011;378(9806):1874–84.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Alana Guidry and Ximena Garcia for their assistance in the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.S., Hodgins, D.C. A Review of the Evidence for Considering Gambling Disorder (and Other Behavioral Addictions) as a Disorder Due to Addictive Behaviors in the ICD-11: a Focus on Case-Control Studies. Curr Addict Rep 6, 273–295 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-019-00256-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-019-00256-0