Abstract
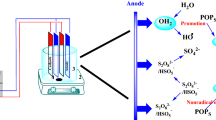
Current work deals with the treatment of leachate nanofiltration concentrate which was exposed to ultrafiltration membrane treatment following anaerobic biological process and nitrification–dentrification process before. Advanced electrocoagulation processes [electro-Fenton (EF) and electro-persulfate (EF)] were applied to the wastewater characterized by high inert COD content arising from resistant organic matter. Response surface methodology and central composite design were employed for modeling and optimizing the processes. Adequacy of the model was examined by application of variance analysis that verified the conformity of experimental and predicted data. Under statistically obtained optimized conditions for COD removal (H2O2/COD ratio 1.42, current 2.27 A, pH 2.9, and reaction time 30.3 min for EF; and S2O8−2/COD ratio 1.72, current 1.26 A, pH 5.0 and reaction time 34.8 min for EP processes), predicted COD removal efficiencies were determined to be 67.1% and 72.6% for EF and EP treatments, respectively. By performing experimental sets for validation, 60.8% and 71.4% COD removals through EF and EP processes were obtained under these conditions. NF concentrate COD fractions were also determined before and after treatment processes. Soluble COD fraction increased from 71.4 to 83.2% and 87.7% whereas biodegradable COD fraction increased from 12.2 to 19.2% and 32.5% after EF and EP processes, respectively. Results of the study showed that both EF and EP processes were efficient alternatives for leachate NF concentrate treatment but EP process can be preferred due to lower energy consumption.
Article Highlights
-
Electro-Fenton and Electro-Persulfate processes were applied for inert COD removal from leachate nanofiltration concentrate.
-
Response surface methodology approach using Central Composite Design was employed for modelling.
-
Under statistically optimized conditions 60.8% and 71.4% COD removals through EF and EP processes were obtained.
-
Biodegradable COD fraction increased and insoluble COD fraction was significantly converted to soluble fraction.
-
Total cost of EF process (5.0 €/ m3) was found to be higher than that of and EP process (2.8 €/ m3).








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Adj-R2 :
-
Adjusted R2
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- CCD:
-
Central composite design
- R 2 :
-
Determination coefficient
- EC:
-
Electrocoagulation
- EF:
-
Electro-Fenton
- EP:
-
Electro-persulfate
- HO∙:
-
Hydroxyl radicals
- MF:
-
Microfiltration
- NF:
-
Nanofiltration
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodolody
- SO4·− :
-
Sulfate radical
- UF:
-
Ultrafiltration
References
Abu Amr SS, Aziz HA, Adlan MN, Aziz SQ (2013) Effect of ozone and ozone/fenton in the advanced oxidation process on biodegradable characteristics of semi-aerobic stabilized leachate. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 41:148–152. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201200005
Abu Amr SS, Aziz HA, Adlan MN, Alkasseh JMA (2014) Effect of ozone and ozone/persulfate processes on biodegradable and soluble characteristics of semiaerobic stabilized leachate. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 33:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.11779
Ahmad AL, Ismail S, Bhatia S (2005) Optimization of coagulation-flocculation process for palm oil mill effluent using response surface methodology. Environ Sci Technol 39:2828–2834. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0498080
Ahmadi M, Ghanbari F (2016) Optimizing COD removal from greywater by photoelectro-persulfate process using Box-Behnken design: assessment of effluent quality and electrical energy consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:19350–19361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7139-6
Ahmadi M, Ghanbari F, Moradi M (2015) Photocatalysis assisted by peroxymonosulfate and persulfate for benzotriazole degradation: effect of pH on sulfate and hydroxyl radicals. Water Sci Technol 72:2095–2102. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.437
Ahmadzadeh S, Dolatabadi M (2018) Modeling and kinetics study of electrochemical peroxidation process for mineralization of bisphenol A; a new paradigm for groundwater treatment. J Mol Liq 254:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.080
Ahmed M, Shayya WH, Hoey D et al (2000) Use of evaporation ponds for brine disposal in desalination plants. Desalination 130:155–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(00)00083-7
Akbari S, Ghanbari F, Moradi M (2016) Bisphenol A degradation in aqueous solutions by electrogenerated ferrous ion activated ozone, hydrogen peroxide and persulfate: applying low current density for oxidation mechanism. Chem Eng J 294:298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.106
Akyol A, Can OT, Demirbas E, Kobya M (2013) A comparative study of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton for treatment of wastewater from liquid organic fertilizer plant. Sep Purif Technol 112:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.03.036
Aleboyeh A, Daneshvar N, Kasiri MB (2008) Optimization of C.I. Acid Red 14 azo dye removal by electrocoagulation batch process with response surface methodology. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 47:827–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2007.01.033
Amani-Ghadim AR, Aber S, Olad A, Ashassi-Sorkhabi H (2013) Optimization of electrocoagulation process for removal of an azo dye using response surface methodology and investigation on the occurrence of destructive side reactions. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 64:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2012.10.012
APHA (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn. APHA, Washington, DC, USA. Am Water Work Assoc Public Work Assoc Environ Fed. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.51.6.940-a
Bashir MJ, Lim JH, Abu Amr SS et al (2019) Post treatment of palm oil mill effluent using electro-coagulation-peroxidation (ECP) technique. J Clean Prod 208:716–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.073
Biglarijoo N, Mirbagheri SA, Ehteshami M, Ghaznavi SM (2016) Optimization of Fenton process using response surface methodology and analytic hierarchy process for landfill leachate treatment. Process Saf Environ 104:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.08.019
Bilgili MS, Demir A, Akkaya E, Ozkaya B (2008) COD fractions of leachate from aerobic and anaerobic pilot scale landfill reactors. J Hazard Mater 158:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.055
Chan YJ, Chong MF, Law CL, Hassell DG (2009) A review on anaerobic–aerobic treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Chem Eng J 155:1–18
Chelme-Ayala P, Smith DW, El-Din MG (2009) Membrane concentrate management options: a comprehensive critical review. Can J Civ Eng 36:1107–1119
Cui Y-H, Xue W-J, Yang S-Q, Tu J-L, Guo X-L, Liu Z-Q (2018) Electrochemical/peroxydisulfate/Fe3+ treatment of landfill leachate nanofiltration concentrate after ultrafiltration. Chem Eng J 353:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.101
Devi P, Das U, Dalai AK (2016) In-situ chemical oxidation: principle and applications of peroxide and persulfate treatments in wastewater systems. Sci Total Environ 571:643–657
Fernandes A, Labiadh L, Ciríaco L, José Pacheco M, Gadri A, Ammar S, Lopes A (2017) Electro-Fenton oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate from sanitary landfill leachate: evaluation of operational parameters. Chemosphere 184:1223–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.088
Fernandes A, Chamem O, José Pacheco M, Ciríaco L, Zairi M, Lopes A (2019) Performance of electrochemical processes in the treatment of reverse osmosis concentrates of sanitary landfill leachate. Molecules 24:2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162905
Gengec E, Kobya M, Demirbas E et al (2012) Optimization of baker’s yeast wastewater using response surface methodology by electrocoagulation. Desalination 286:200–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.023
Gunst RF, Myers RH, Montgomery DC (1996) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. Technometrics 38:285. https://doi.org/10.2307/1270613
Guvenc SY, Dincer K, Varank G (2019) Performance of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton processes for treatment of nanofiltration concentrate of biologically stabilized landfill leachate. J Water Process Eng 31:100863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100863
Harrelkas F, Azizi A, Yaacoubi A et al (2009) Treatment of textile dye effluents using coagulation-flocculation coupled with membrane processes or adsorption on powdered activated carbon. Desalination 235:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.02.012
Hazime R, Nguyen QH, Ferronato C et al (2014) Comparative study of imazalil degradation in three systems: UV/TiO2, UV/K2S2O8 and UV/TiO2/K2S2O8. Appl Catal B Environ 144:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.001
He R, Wei XM, Chen M et al (2016) Effects of concentrated leachate injection modes on stabilization of landfilled waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3333–3341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5554-8
Hilles AH, Abu Amr SS, Hussein RA et al (2015) Effect of persulfate and persulfate/H2O2 on biodegradability of an anaerobic stabilized landfill leachate. Waste Manag 44:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.07.046
Hu Y, Lu Y, Liu G, Luo H, Zhang R, Cai X (2018) Effect of the structure of stacked electro-Fenton reactor on treating nanofiltration concentrate of landfill leachate. Chemosphere 202:191–197
Jaafarzadeh N, Omidinasab M, Ghanbari F (2016) Combined electrocoagulation and UV-based sulfate radical oxidation processes for treatment of pulp and paper wastewater. Process Saf Environ Prot 102:462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.04.019
Kabdaşli I, Arslan T, Arslan-Alaton I et al (2010) Organic matter and heavy metal removals from complexed metal plating effluent by the combined electrocoagulation/Fenton process. Water Sci Technol 61:2617–2624. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.202
Khataee AR (2009) Application of central composite design for the optimization of photo-destruction of a textile dye using UV/S2O82-process. Pol J Chem Technol 11:38–45. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10026-009-0041-y
Khataee AR, Zarei M, Asl SK (2010) Photocatalytic treatment of a dye solution using immobilized TiO2 nanoparticles combined with photoelectro-Fenton process: optimization of operational parameters. J Electroanal Chem 648:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2010.07.017
Kumar J, Bansal A (2013) Photocatalytic degradation in annular reactor: modelization and optimization using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and response surface methodology (RSM). J Environ Chem Eng 1:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.06.002
Kumar M, Ponselvan FIA, Malviya JR et al (2009) Treatment of bio-digester effluent by electrocoagulation using iron electrodes. J Hazard Mater 165:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.041
Labiadh L, Fernandes A, Ciríaco L, José Pacheco M, Gadri A, Ammar S, Lopes A (2016) Electrochemical treatment of concentrate from reverse osmosis of sanitary landfill leachate. J Environ Manag 181:515–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.06.069
Li Z, Zhou S, Qiu J (2007) Combined treatment of landfill leachate by biological and membrane filtration technology. Environ Eng Sci 24:1245–1256. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2006.0169
Li J, Ai Z, Zhang L (2009) Design of a neutral electro-Fenton system with Fe@Fe2O3/ACF composite cathode for wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 164:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.109
Liu H, Li XZ, Leng YJ, Wang C (2007) Kinetic modeling of electro-Fenton reaction in aqueous solution. Water Res 41:1161–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.12.006
Malakootian M, Ahmadian M (2019) Ciprofloxacin removal by electro-activated persulfate in aqueous solution using iron electrodes. Appl Water Sci 9:140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1024-7
Martins AF, Wilde ML, Vasconcelos TG, Henriques DM (2006) Nonylphenol polyethoxylate degradation by means of electrocoagulation and electrochemical Fenton. Sep Purif Technol 50:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2005.11.032
Massart DL, Vandeginste BGM, Buydens LMC, De Jong S, Lewi PJ, Smeyers-Verbeke J (1998) Handbook of chemometrics and qualimetrics: part A. In: Data handling in science and technology, 52, 8: 302A. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Mohajeri L, Aziz HA, Isa MH, Zahed MA (2010a) A statistical experiment design approach for optimizing biodegradation of weathered crude oil in coastal sediments. Bioresour Technol 101:893–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.013
Mohajeri S, Aziz HA, Isa MH et al (2010b) Statistical optimization of process parameters for landfill leachate treatment using electro-Fenton technique. J Hazard Mater 176:749–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.099
Nair AT, Makwana AR, Ahammed MM (2014) The use of response surface methodology for modelling and analysis of water and wastewater treatment processes: a review. Water Sci Technol 69(3):464–478. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.733
Nam SN, Cho H, Han J, Her N, Yoon J (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of acesulfame K: optimization using the Box–Behnken design (BBD). Process Saf Environ 113:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.09.002
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R (2012) Trends in electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment: an overview. Desalination 299:1–15
Ölmez T (2009) The optimization of Cr(VI) reduction and removal by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater 162:1371–1378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.017
Olmez-Hanci T, Arslan-Alaton I, Genc B (2013) Bisphenol A treatment by the hot persulfate process: Oxidation products and acute toxicity. J Hazard Mater 263:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.032
Qiang Z, Chang JH, Huang CP (2003) Electrochemical regeneration of Fe2+ in Fenton oxidation processes. Water Res 37:1308–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00461-X
Rahmani AR, Rezaeivahidian H, Almasi M, Shabanlo A, Almasi H (2016) A comparative study on the removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by electro–Fenton and electro–persulfate processes using iron electrodes. Res Chem Intermediates 42:1441–1450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2095-1
Rao YF, Qu L, Yang H, Chu W (2014) Degradation of carbamazepine by Fe(II)-activated persulfate process. J Hazard Mater 268:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.010
Rastkari N, Eslami A, Nasseri S et al (2017) Optimizing parameters on nanophotocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen using UVC/ZnO processes by response surface methodology. Pol J Environ Stud 26:785–794. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/64931
Sabour MR, Amiri A (2017) Comparative study of ANN and RSM for simultaneous optimization of multiple targets in Fenton treatment of landfill leachate. Waste Manag 65:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.03.048
Saini R, Kumar P (2016) Optimization of chlorpyrifos degradation by Fenton oxidation using CCD and ANFIS computing technique. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2952–2963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.06.003
Silveira JE, Garcia-Costa AL, Cardoso TO, Zazo JA, Casas JA (2017) Indirect decolorization of azo dye Disperse Blue 3 by electro-activated persulfate. Electrochim Acta 258:927–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.11.143
Silveira JE, Cardoso TO, Barreto-Rodrigues M et al (2018) Electro activation of persulfate using iron sheet as low-cost electrode: the role of the operating conditions. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 39:1208–1216. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1323960
Soomro GS, Qu C, Ren N, Meng S, Li X, Liang D, Zhang S, Li Y (2020) Efficient removal of refractory organics in landfill leachate concentrates by electrocoagulation in tandem with simultaneous electro-oxidation and insitu peroxone. Environ Res 183:109249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109249
Sridhar R, Sivakumar V, Prince Immanuel V, Prakash Maran J (2011) Treatment of pulp and paper industry bleaching effluent by electrocoagulant process. J Hazard Mater 186:1495–1502
Sun M, Chen F, Qu J et al (2015) Optimization and control of Electro-Fenton process by pH inflection points: a case of treating acrylic fiber manufacturing wastewater. Chem Eng J 269:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.115
Van Der Bruggen B, Lejon L, Vandecasteele C (2003) Reuse, treatment, and discharge of the concentrate of pressure-driven membrane processes. Environ Sci Technol 37:3733–3738
Varank G, Sabuncu ME (2015) Application of central composite design approach for dairy wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation using iron and aluminum electrodes: modeling and optimization. Desalin Water Treat 56:33–54
Varank G, Guvenc SY, Demir A (2020) Electro-activated peroxymonosulfate and peroxydisulfate oxidation of leachate nanofiltration concentrate: multiple-response optimization. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:2707–2720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02651-x
Virkutyte J, Rokhina E, Jegatheesan V (2010) Optimisation of electro-Fenton denitrification of a model wastewater using a response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 101:1440–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.041
Wang G, Wu T, Li Y, Sun D, Wang Y, Huang X, Zhang G, Liu R (2012a) Removal of ampicillin sodium in solution using activated carbon adsorption integrated with H2O2 oxidation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87:623–628. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2754
Wang Y, Li X, Zhen L, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Wang C (2012b) Electro-Fenton treatment of concentrates generated in nanofiltration of biologically pretreated landfill leachate. J Hazard Mater 229–230:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.108
Wang H, Wang Y, Li X et al (2016) Removal of humic substances from reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) concentrated leachate using continuously ozone generation-reaction treatment equipment. Waste Manag 56:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.07.040
Wang H, Wang Y, Lou Z et al (2017) The degradation processes of refractory substances in nanofiltration concentrated leachate using micro-ozonation. Waste Manag 69:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.048
Wong LP, Isa MH, Bashir MJK (2018) Disintegration of palm oil mill effluent organic solids by ultrasonication: optimization by response surface methodology. Process Saf Environ Prot 114:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.12.012
Xue W-J, Cui Y-H, Liu Z-Q, Yang S-Q, Li J-Y, Guo X-L (2020) Treatment of landfill leachate nanofiltration concentrate after ultrafiltration by electrochemically assisted heat activation of peroxydisulfate. Sep Purif Technol 231:115928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115928
Yang W, Cicek N, Ilg J (2006) State-of-the-art of membrane bioreactors: worldwide research and commercial applications in North America. J Memb Sci 270:201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2005.07.010
Zhang H, Choi HJ, Canazo P, Huang CP (2009) Multivariate approach to the Fenton process for the treatment of landfill leachate. J Hazard Mater 161:1306–1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.126
Zhou B, Yu Z, Wei Q, Long H, Xie Y, Wang Y (2016) Electrochemical oxidation of biological pretreated and membraneseparated landfill leachate concentrates on boron doped diamondanode. Appl Surf Sci 377:406–415
Zhou X, Hou Z, Lv L et al (2020) Electro-Fenton with peroxi-coagulation as a feasible pre-treatment for high-strength refractory coke plant wastewater: parameters optimization, removal behavior and kinetics analysis. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124649
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by “Yildiz Technical University-The Scientific Research Projects Coordinatorship” with the research project number of FBA-2018-3282.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varank, G., Yazici Guvenc, S., Dincer, K. et al. Concentrated Leachate Treatment by Electro-Fenton and Electro-Persulfate Processes Using Central Composite Design. Int J Environ Res 14, 439–461 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00269-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00269-y