Abstract
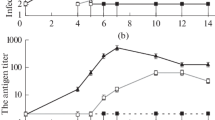
A human continuous cell line (huGK-14) within a lineage of passaged cultures was investigated in the mode of integration and expression of hepatitis B virus (HBV) genes. HBV DNA was integrated in eight different sites of the cellular DNA, in each of which HBV genome was rearranged, fragmented, and/or partly deleted. Complete HBV genome that may lead to production of infectious virus particles was not detected in the cells nor in the culture medium. Clones of cDNA containing a complete coding frame for small HBs antigen protein (type adr) were obtained from mRNA of the cells. The cells were stable over the period of six months of cultivation and more than 60 population doublings in the mode of HBV integration and HBs mRNA expression.
These results provide substantial evidence for the absence of an ability for the integrated DNA to create an infectious product in the cell; for the stable production of HBs mRNA from the cells, and suggest the usefulness of this cell line as a substrate for HBV vaccine production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABMJ (1993) Association of biologicals manufacturers of Japan. Minimum requirement for biological products, Tokyo. pp. 11–16.
Alexander J, Macnab G and Saunders R (1978) Studies on in vitro production of hepatitis B surface antigen by a human hepatoma cell line. Perspectives in Virology 10: 103–120.
Barin F, Maupas P, Coursaget P, Goudeau A and Chiron JP (1981) An alternative vaccine against hepatitis B produced from a human hepatoma cell line, in: hepatitis B vaccine, Maupas P and Guestry P, ed., 263–266, Elsevier/North-Holland, Biomedical Press. Amsterdam.
Barin F, Goudeau A, Brachot C, Romet-Lemonne J, Sureau C, Lesage G (1983) Further studies on production and characterization of HBsAg derived from a human hepatoma cell line (PLC/PRF/5). Develop. Biol. Stand. 54: 81–92.
Brechot C, Hadchouel M, Scotto J, Fonck M, Potet F, Vyas GN and Tiollais P (1981) State of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes of patients with hepetitis B surface antigen-positive and-negative liver diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78: 3906–3910.
Brechot C, Pourcel C, Hadchouel M, Dejean A, Louise A, Scotto J and Tiollais P (1982) State of hepatitis B virus DNA in liver diseases. Hepatology 2: 27S–34S.
CBER (1993) Points to consider in the characterization of cell lines used to produce biologicals, US. Food and Drug Administration, Bethesda, MD.
CBER (1996) FDA guidance concerningg demonstration of comparability of human biological products, including therapeutic biotechnology-derived products. US. Food and Drug Administration, Bethesda, MD.
Chakraborty PR, Ruiz-Opazo N, Shouval D and Shafritz DA (1980) Identification of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA and expression of viral RNA in an HBsAg-producing human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Nature 286: 531–533.
Choo K-B, Liu M-S, Chang P-C, Wu S-M, Su M-W, Pan C-C and Han S-H (1986) Analysis of six integrated hepatitis B virus sequences cloned from the cellular DNA of a human hepatocellular carcinoma. Virology 154: 405–408.
Dejean A, Brechot C, Tiollais P and Wain-Hobson S (1983) Characterization of integrated hepatitis B viral DNA cloned from a human hepatoma and the hepatoma-derived cell line PLC/PRF/5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80: 2505–2509.
Dejean A, Sonigo P, Wain-Hobson S and Tiollais P (1984) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81: 5350–5354.
Dejean A and de The H (1990) Hepatitis B Virus as an insertional mutagen in a human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Med. 7: 213–222.
Edman JC, Gray P, Valenzuela P, Rall LB and Rutter WJ (1980) Integration of hepatitis B virus sequences and their expression in a human hepatoma cell. Nature 286: 535–538.
Fujiyama A, Miyanohara A, Nozaki C, Yoneyama T, Ohtomo N and Matsubara K (1983) Cloning and structural analysis of hepatitis B virus DNAs. subtype adr. Nucl. Acids Res. 11: 4601–4610.
Ganem D and Varmus HE (1987) The molecular Biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 56: 651–693.
Garnier A, Cote J, Nadeau I, Kamen A and Massie B (1994) Scaleup of the adenovirus expression system for the production of recombinant protein in human 293S cells. Cytotechnology 15: 145–155.
Graham FL (1987) Growth of 293 cells in suspension culture. J. Gen. Virol. 68: 937–940.
Hattori M and Sakai Y (1986) Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Analyt. Biochem. 152: 232–238.
Hayflick L (1989) History of cell substrates used for human biologicals. Develop. Biol. Stand. 70: 11–26.
Huh N and Utakoji T (1981) production of HBs-antigen by two new human hepatoma cell lines and its enhancement by dexamethasone. Jpn. J. Canc. Res. 72: 178–179.
Katsuta H and Takaoka T (1978) Protein and liped-free synthetic media for the cultivation of mammalian cells in tissue culture. In: Nutritional Requirements of cultured cells. ed. by H. Katsuta, pp. 257–275, Japn. Sci. Soc. press, Tokyo and University Park Press, Baltimore.
Kobayashi M and Koike K (1984) Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatitis B virus DNA of subtype adr and its conserved gene organization. Gene 30: 227–232.
Koike K, Kobayashi M, Mizusawa H, Yoshida E, Yaginuma K and Taira M (1983) Rearrangement of the surface antigen gene of hepatitis B virus integrated in the human hepatoma cell lines. Nucl. Acid. Res. 11: 5391–5402.
Koike K, Yaginuma K, Mizusawa H, Kobayashi M (1985) Structure of integrated HBV DNA in humnan hepatomas. In: Nishioka K, Brunberg B, Ishida N and Koike K (eds.) Hepatitis viruses and hepatocellular carcinoma: Approaches through molecular biology and ecology, pp. 99–115. Academic Press.
Koike K, Yoshida E, Katagiri K, Kata-yanagi M, Oda M, Tsunoo H, Yaginuma K and Kobayashi M (1987) Production of hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles by the human hepatoma cell line huGK-14 in a serum-free medium. Jpn. J. Canc. Res. 7: 1341–1346.26.
Koshy R, Koch S, von Loringhoven AF, Kahmann R, Murray K and Hofschneider PH (1983) Integration of Hepatitis B virus DNA: Evidence for integration in the single-stranded gap. Cell 34: 215–223.
MacNab GM, Alexander JJ, Lecatsas G, Bey EM and Urbanowicz JM (1976) Hepatitis B surface antigen produced by a human hepatoma cell line. Br. J. cancer 34: 509–515.
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF and Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory mannual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Gold Spring Harbor, NY.
Marion PL, Salazar FH, Alexander JJ and Robinson WS (1979) Polypeptides of hepatitis B virus surface antigen produced by a hepatome cell line. J. Virol. 32: 796–802.
Matsubara K and Tokino T (1990) Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA and its implications for hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol. Biol. Med. 7: 243–260.
McAleer WJ, Markus HZ, Bailey FJ, Herman AC, Harder BJ, Wampler ED, Miller WJ, Keller PM, Buynak EB and Hilleman MR (1983) Production of purified hepatitis B surface antigen from Alexander hepatoma cells grown in artificial capillary units. J. Virol. Methods 7: 263–271.
Mizusawa H, Taira M, Yaginuma K, Kobayashi M, Yoshida E and Koike K (1985) Inversely repeating integrated hepatitis B virus DNA and cellular flanking sequences in the human hepatomaderived cell line huSP. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82: 208–212.
Ono Y, Onda H, Sasada R, Igarashi K, Sugino Y and Nishioka K (1983) The complete nucleotide sequence of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA: subtype adr and adw. Nucl. Acid Res. 11: 1747–1757.
Pearson J (1992) Changing issues of quality control: Diploid and non-diploid cell lines. Develop. Biol. Stand. 76: 13–17.
Petricciani JC (1992) Cell line issues: Historical and future p perspectives. develop. Biol. Stand. 76: 5–11.
Petricciani JC and Horaud FN (1995) DNA, Dragons and sanity. Biologicals 23: 233–238.
Rivkina MB, Lunin VG, Mahov AM, Tikchonenko TI and Kukain RA (1988) Nucleotide sequence of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA and human flanking regions in the genome of the PLC/PRF/5 cell line. Gene 64: 285–296.
Shafritz D and Kew MC (1981) Identification of integrated Hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology 1: 1–8.
Shafritz DA, Shauval D, Sherman HI, Hadziyannis SJ and Kew MC (1981) Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the genome of liver cells in chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma, N. Engl. J. Med. 305: 1067–1073.
Skelly J, Copeland JA, Howard CR and Zuckerman AJ (1979) Hepatitis B surface antigen produced by a human hepatoma cell line. Nature 282: 617–618.
Takada S, Gotoh Y, Hayashi S, Yoshida M and Koike K (1990) Structural rearrangement of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA as well as cellular flanking DNA is present in chronically infected hepatic tissues. J Virology 64: 822–828.
Tiollais P, Pourcel C and Dejean A (1985) The hepatitis B virus. Nature 317: 489–495.
Tokino T, Fukushige S, Nakamura T, Nagaya T, Murotsu T, Shiga K, Aoki N and Matsubara K (1987) Chromosomal translocation and inverted duplication associated with integrated hepatitis B virus in hepatocellular carcinomas. J. virology 61: 3848–3854.
Williams GM and Gunn JM (1974) Long-term culture of adult rat liver epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 89: 139–142.
Yaginuma K, Kobayashi H, Yoshida E, Kobayashi M and Koike K (1984) Direct evidence for the expression of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA in human hepatoma tissue. Gann 75: 743–746.
Zerial M, Salinas J, Filipski J and Bernardi G (1986) Genomic localization of hepatitis B virus in a human hepatoma cell line. Nucl. Acid. Res. 14: 8373–8386.
Ziemer M, Garcia P, Shaul Y and Rutter WJ (1985) Sequence of hepatitis B virus DNA incorporated into the genome of human hepatoma cell line. J. virology 53: 885–892.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamichi, N., Noda, A., Yonezu, T. et al. Structure and expression of integrated hepatitis B virus genes in an HBs antigen producing human cell line (huGK-14). Cytotechnology 25, 61–70 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007924119018
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007924119018