Abstract
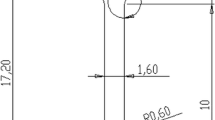
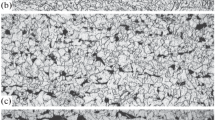
When hot rolled tough pitch copper is made from copper scraps, lead is intentionally or unintentionally added to the melt. The major role of this lead seems to be the removal of metallic tin by the formation of PbO–SnO2. A continuously cast and hot rolled copper rod was preheated at temperatures between 673–1173 K for 1 h prior to cold drawing. The maximum diameter of the PbO–SnO2, of 1–2 μm, was obtained by preheating at 873 K. This preheating temperature also produced the maximum decrease in the recrystallization temperature and the maximum electrical conductivity of the 89.4% cold drawn wire within the investigated experimental range. This can be attributed to a decrease in the dissolved impurity concentration due to the growth of PbO–SnO2 particles at that temperature. The decrease in recrystallization temperature enhanced the room temperature multiple upset weldability. When preheated at 1173 K, Zn2SnO4 particles were formed, but the recrystallization temperature increased and the electrical conductivity decreased due to the dissolution of PbO–SnO2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. SMART and A. A. SMITH, Trans. AIME. 147 (1942) 48.
Idem, ibid. 152 (1943) 103.
Idem, ibid. 166 (1946) 144.
M. FELLER-KNIEPMEIER and K. SCHWARTZKOPFF, Acta Metall. 17 (1969) 497.
S. A. REID and C. J. BALL, Metals Tech. 1 (1974) 41.
V. J. MARINO, M. YOKELSON and G. J. FISCHER, Wire J. 42 (1975) 60.
Y. T. HSU and B. O’REILLY, J. Met. 29 (1977) 21.
C. H. PITT, P. L. TAYLER and D. L. VAN WAGONER, Metall. Trans. 10A (1979) 809.
J. S. SMART, in “Copper: The Metal, its Alloys and Compounds”, edited by A. Butts (Reinhold, New York, 1954) p. 410.
S. AOYAMA, M. ONUKI, Y. MIYAKE and R. URAO, J. Jpn Inst. Metals 51 (1987) 858.
Idem, ibid. 53 (1989) 452.
Idem, ibid. 55 (1991) 324.
Idem, J. Mater. Sci. 26 (1991) 3775.
R. URAO, S. AOYAMA, M. KAMINAGA, M. ONUKI and Y. MIYAKE, Jpn Inst Metals 54 (1990) 1030.
R. L. O'BRIEN "Welding Handbook"; (American Welding Society, New York, 1991).
G. E. DIETER, “Mechanical Metallurgy” (McGraw Hill, New York, 1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WON, Y.M., OH, K.H. Effect of preheating on the mechanical properties of tough pitch copper made from copper scraps. Journal of Materials Science 32, 2045–2054 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018510402818
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018510402818