Abstract
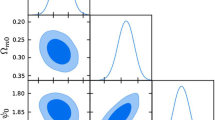
We present a scalar perturbation for the ΛCDM model, which breaks the isotropic symmetry of the universe. Based on the Union2 data, the least-χ 2 fit of the scalar perturbed ΛCDM model shows that the universe has a preferred direction (l,b)=(287∘±25∘,11∘±22∘). The magnitude of scalar perturbation is about −2.3×10−5. The scalar perturbation for the ΛCDM model implies a peculiar velocity, which is perpendicular to the radial direction. We show that the maximum peculiar velocities at redshift z=0.15 and z=0.015 equal to 73±28 km s−1 and 1099±427 km s−1, respectively. They are compatible with the constraints on the peculiar velocity given by the Planck Collaboration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Sahni, Class. Quantum Gravity 19, 3435 (2002)
T. Padmanabhan, Phys. Rep. 380, 235 (2003)
E. Komatsu et al. (WMAP Collaboration), Astrophys. J. Suppl. 192, 18 (2011)
Planck Collaboration, arXiv:1303.5062
N. Suzuki et al., Astrophys. J. 746, 85 (2012)
L. Perivolaropoulos, arXiv:1104.0539
I. Antoniou, L. Perivolaropoulos, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1012, 012 (2012)
R. Watkins, H.A. Feldman, M.J. Hu dson, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 392, 743 (2009)
G. Hinshaw et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. 180, 225 (2009)
Planck Collaboration, arXiv:1303.5083
T. Koivisto, D.F. Mota, Phys. Rev. D 73, 083502 (2006)
S. Alexander, T. Biswas, A. Notari, D. Vaid, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 0909, 025 (2009)
J. Garcia-Bellido, T. Haugboelle, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 0804, 003 (2008)
E. Akofor et al., J. High Energy Phys. 0805, 092 (2008)
T.S. Koivisto, D.F. Mota, M. Quartin, T.G. Zlosnik, Phys. Rev. D 83, 023509 (2011)
Z. Chang, M.-H. Li, X. Li, S. Wang, Eur. Phys. J. C 73, 2459 (2013)
S. Weinberg, Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity (Wiley, New York, 1972)
Planck Collaboration, arXiv:1303.5090
R. Amanullah et al., Astrophys. J. 716, 712 (2010)
A. Kogut et al., Astrophys. J. 419, 1 (1993)
R.-G. Cai, Z.-L. Tuo, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1202, 004 (2012)
B. Kalus et al., Astron. Astrophys. 553, A56 (2013)
R.G. Cai, Y.Z. Ma, B. Tang, Z.L. Tuo, Phys. Rev. D 87, 123522 (2013)
K. Rosquist, R.T. Jantzen, Phys. Rep. 166, 89 (1988)
C.W. Misner, K.S. Thorne, J.A. Wheeler, Gravitation (Freeman, San Francisco, 1973)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Y.G. Jiang for useful discussions. Project 11375203 and 11305181 supported by NSFC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Lin, HN., Wang, S. et al. ΛCDM model with a scalar perturbation vs. preferred direction of the universe. Eur. Phys. J. C 73, 2653 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-013-2653-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-013-2653-x