Abstract
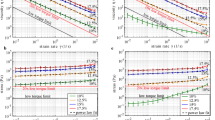
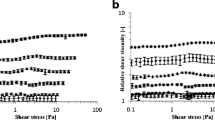
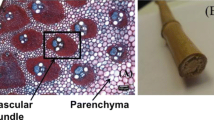
Corn stover is currently being evaluated as a feedstock for ethanol production. The corn stover suspensions fed to reactors typically range between 10 and 40% solids. To simulate and design bioreactors for processing highly loaded corn stover suspensions, the rheologic properties of the suspension must be measured. In systems with suspended solids, rheologic measurements are difficult to perform owing to settling in the measurement devices. In this study, viscosities of corn stover suspensions were measured using a helical ribbon impeller viscometer. A calibration procedure is required for the impeller method in order to obtain the shear rate constant, k, which is dependent on the geometry of the measurement system. The corn stover suspensions are described using a power law flow model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McMillan, J. D. (1997), Renewable Energy 10(2/3), 295–302.
Wenzl, H. F. J. (1996), The Chemical Technology of Wood, Academic, New York, NY.
Hayn, M., Steiner, W., Klinger, R., Steinmueller, H., Sinner, M., and Esterbauer, H. (1993), in Bioconversion of Forest and Agricultural Plant Residues, Saddler, J. N., ed., CAB, Wallingford, UK, pp. 33–72.
Esteghlalian, A., Hashimoto, A. G., Fenske, J. J., and Penner, M. (1997), Bioresour. Technol. 59, 129–136.
Ranatunga, T. D., Jervis, J., Helm, R. F., McMillan, J. D., and Wooley, R. J. (2000), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 27, 240–247.
Svihla, C. K., Dronawat, S. N., and Hanley, T. R. (1995), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 51/52, 355–366.
Allen, D. G. and Robinson, C. W. (1990), Chem. Eng. Sci. 45(1), 37–48.
Kemblowski, L. and Kristiansen, B. (1986), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 28, 1474–1483.
Metz, B., Kossen, N. W. F., and Van Suijdam, J. C. (1979), Adv. Biochem. Eng. 11, 103–155.
Charles, M. (1978), Adv. Biochem. Eng. 8, 1–62.
Dronawat, S. N., Rieth, T. C., Svihla, C. K., and Hanley, T. R. (1996) in Proceedings of the 5th World Congress of Chemical Engineering, vol. 1, AIChE, New York, NY, pp. 629–633.
Svihla, C. K., Dronawat, S. N., Donnely, J. A., Rieth, T. C., and Hanley, T. R. (1997) Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 63/65, 375–385.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pimenova, N.V., Hanley, T.R. Measurement of rheological properties of corn stover suspensions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 106, 383–392 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:106:1-3:383
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:106:1-3:383