Abstract
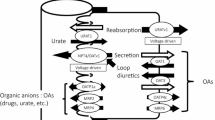
Organic anions of diverse chemical structures are secreted in renal proximal tubules. The first step in secretion, uptake of organic anions across the basolateral membrane of tubule cells, is mediated for the polyspecific organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1), which exchanges extracellular organic anions for intracellular α-ketoglutarate or glutarate. OAT1 orthologs cloned from various species show 12 putative transmembrane domains and possess several sites for potential post-translational modification. The gene for the human OAT1 is located on chromosome 11q13.1 and is composed of 10 exons. Alternative splicing within exon 9 gives rise to four variants, two of which (OAT1-1 and OAT1-2) are functional. Following heterologous expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes, flounder renal OAT1 transported p-aminohippurate, glutarate, several diuretics, and the nephrotoxic agent ochratoxin A. Two cationic amino acid residues, lysine 394 and arginine 478, were found to be important for interaction with glutarate. Anionic neurotransmitter metabolites and the heavy-metal chelator, 2,3-dimercaptopropane sulfonate, interacted with the rabbit renal OAT1, which is expressed in kidneys and the retina.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimada, H., Moewes, B., and Burckhardt G. (1987) Indirect coupling to Na+ of p-aminohippuric acid uptake into rat renal basolateral membrane vesicles. Am. J. Physiol. 253, F795-F801.
Van Aubel, R. A. M. H., Masereeuw, R., and Russel, F. G. M. (2000) Molecular pharmacology of renal organic anion transporters. Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol. 279, F216-F232.
Burckhardt, G., Bahn, A., and Wolff, N. A. (2001) Molecular physiology of renal p-aminohippurate secretion. News Physiol. Sci. 16, 114–118.
Sekine, T., Watanabe, N., Hosoyamada, M., Kanai, Y., and Endou, H. (1997) Expression cloning and characterization of a novel multispecific organic anion transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18,526–18,529.
Sweet, D. H., Wolff, N. A., and Pritchard, J. B. (1997) Expression cloning and characterization of ROAT1. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30,088–30,095.
Lopez-Nieto, C. E., You, G. F., Bush, K. T., Barros, E. J. G., Beier, D. R., and Nigam, S. K. (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of NKT, a gene product related to the organic cation transporter family that is almost exclusively expressed in the kidney. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 6471–6478.
Wolff, N. A., Werner, A., Burkhardt, S., and Burckhardt, G. (1997) Expression cloning and characterization of a renal organic anion transporter from winter flounder. FEBS Lett. 417, 287–291.
Reid, G., Wolff, N. A., Dautzenberg, F. M., and Burkhardt, G. (1998) Cloning of a human renal p-aminohippurate transporter, hROAT1. Kidney Blood Pressure Res. 21, 233–237.
Hosoyamada, M., Sekine, T., Kanai, Y., and Endou, H. (1999) Molecular cloning and functional expression of a multispecific organic anion transporter from human kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 276, F122-F128.
Race, J. E., Grassl, S. M., Williams, W. J., and Holtzman, E. J. (1999) Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel human renal organic anion transporters (hOAT1 and hOAT3). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 255, 508–514.
Lu, R., Chan, B. S., and Schuster, V. L. (1999) Cloning of the human kidney PAH transporter: narrow substrate specificity and regulation by protein kinase C. Am. J. Physiol. 276, F295-F303.
George, R. L., Wu, X., Fei, Y.-J., Leibach, F. H., and Ganapathy, V. (1999) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a polyspecific organic anion transporter from Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 291, 596–603.
Burckhardt, G. and Wolff, N. A. (2000) Structure of renal organic anion and cation transporters. Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol. 278, F853-F866.
Sekine, T., Cha, S. H., and Endou, H. (2000) The multispecific organic anion transporter (OAT) family. Pflügers Arch. 440, 337–350.
Tojo, A., Sekine, T., Nakajima, N., Hosoyamada, M., Kanai, Y., Kimura, K., et al. (1999) Immunohistochemical localization of multispecific renal organic anion transporter 1 in rat kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 464–471.
Cha, S. H., Sekine, T., Fukushima, J.-I., Kanai, Y., Kobayashi, Y., Goya, T., et al. (2001) Identification and characterization of human organic anion transporter 3 expressing predominantly in the kidney. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 1277–1286.
Bahn, A., Knabe, M., Wolff, N. A., Hillemann, A., and Burckhardt, G. (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of a renal organic anion transporter of the rabbit (rbOAT1). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 11, 42A.
Bahn, A., Prawitt, D., Buttler, D., Reid, G., Enklaar, T., Wolff, N. A., et al. (2000) Genomic structure and in vivo expression of the human organic anion transporter 1 (hOAT1) gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 275, 623–630.
Buttler, D., Ebbinghaus, C., Hillemann, A., Wolff, N. A., Füzesi, L., Burckhardt, G., et al. (2001) In vivo studies, cloning and functional characterization of the isoforms of the human organic anion transporter 1 (hOAT1). Pflügers Arch. 441, R170.
Wolff, N. A., Grünwald, B., Friedrich, B., Lang, E., Godehardt, S., and Burckhardt, G. (2001) Mutational analysis of fROAT, the flounder renal organic anion transporter. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 12, 2012–2018.
Burckhardt, G., Porth, J., and Wolff, N. A. (1998) Functional and molecular characterization of renal transporters for p-aminohippurate (PAH). Nova Acta Leopoldina 78, 35–40.
Ullrich, K. J. (1997) Renal transporters for organic anions and organic cations. Structural requirements for substrates. J. Membr. Biol. 158, 95–107.
Burckhardt, B. C., Wolff, N. A., and Burckhardt, G. (2000) Electrophysiologic characterization of an anion transporter cloned from Winter flounder kidney (fROAT). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 11, 9–17.
Jariyawat, S., Sekine, T., Takeda, M., Apiwattanakul, N., Kanai, Y., Sophasan, S., et al. (1999) The interaction and transport of β-lactam antibiotics with the cloned rat renal organic anion transporter 1. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 290, 672–677.
Ho, E. S., Lin, D. C., Mendel, D. B., and Cihlar, T. (2000) Cytotoxicity of antiviral nucleotides adefovir and cidofovir is induced by the expression of human renal organic anion transporter 1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 11, 383–393.
Takeda, M., Tojo, A., Sekine, T., Hosoyamada, M., Kanai, Y., and Endou, H. (1999) Role of organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) in cephaloridine (CER)-induced nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 56, 2128–2136.
Mulato, A. S., Ho, E. S., and Cihlar, T. (2000) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs efficiently reduce the transport and cytotoxicity of adefovir mediated by the human renal organic anion transporter 1. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 295, 10–15.
Bahn, A., Quondamatteo, F., Knabe, M., Godehardt, S., Hillemann, A., Herken, G., et al. (2001) Evidences for an important role of the organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) in handling of neurotransmitter metabolites in the eye. Pflügers Arch. 441, R126.
Zalups, R. K. (2000) Molecular interactions with mercury in the kidney. Pharmacol. Rev. 52, 113–143.
Bahn, A., Graber-Neufeld, D. S., Godehardt, S., Knabe, M., Hillemann, A., Burckhardt, G., et al. (2001) Role of organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) in renal heavy metal detoxification. FASEB J. 15, A434.
Koepsell, H., Gorboulev, V., and Arndt, P. (1999) Molecular pharmacology of organic cation transporters in kidney. J. Membr. Biol. 167, 103–117.
Feng, B., Dresser, M. J., Shu, Y., Johns, S. J., and Giacomini, K. M. (2001) Arginine 454 and lysine 370 are essential for the anion specificity of the organic anion transporter, rOAT3. Biochemistry 40, 5511–5520.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burckhardt, G., Wolff, N.A. & Bahn, A. Molecular characterization of the renal organic anion transporter 1. Cell Biochem Biophys 36, 169–174 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:36:2-3:169
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:36:2-3:169